Content
- What Is Eclipse?
- How Does Eclipse Work?
- Why Modularise Rollups?
- The Future of Eclipse
- Conclusion
- About Zerocap
- DISCLAIMER
- FAQs
- What is Eclipse and how does it relate to blockchain architecture?
- How does Eclipse address the blockchain trilemma?
- What is the role of virtual machines in the Eclipse network?
- What is the future of Eclipse?
- What are the benefits of Eclipse's modular rollup framework?
4 May, 23
What is Eclipse?

- What Is Eclipse?
- How Does Eclipse Work?
- Why Modularise Rollups?
- The Future of Eclipse
- Conclusion
- About Zerocap
- DISCLAIMER
- FAQs
- What is Eclipse and how does it relate to blockchain architecture?
- How does Eclipse address the blockchain trilemma?
- What is the role of virtual machines in the Eclipse network?
- What is the future of Eclipse?
- What are the benefits of Eclipse's modular rollup framework?
Although the totality of blockchain architecture often comprises a labyrinthine structure, the present norm simplifies it to four layers: execution, settlement, consensus and data availability. These layers act similarly to traditional payment systems with an execution layer (the payment service), a settlement layer (the bank’s payment processor) and a data availability layer (the bank’s records). Within its own modular architecture, Eclipse acts as the payment processor, responsible for validating transactions and connecting the base layer to the application layer. Eclipse’s unique approach to deploying rollups enables the seamless customisation of the base and application layers, similar to picking your own payment service and bank. In doing so, the Eclipse network can bring unparalleled efficiency and versatility to the world of decentralised systems.

What Is Eclipse?
Traditionally, blockchains handle all operations necessary for their functioning within a single network. These operations include execution, settlement, consensus, and data availability. However, this approach reduces efficiency and leads to the blockchain trilemma, a phenomenon that causes layer 1s to compromise between decentralisation, security, and scalability. To address this issue, modular blockchain architectures offer a solution by creating independent chains or modules with specialised functions. Modular blockchains offer scalability, efficiency, and customization that cannot be achieved in monolithic blockchains. Eclipse leverages blockchain modularity to maximise efficiency and flexibility.
In essence, Eclipse serves as a platform for the development of modular rollups. A rollup is a layer 2 scaling solution that executes transactions off-chain before bundling them into a single transaction and executing them as a batch on the base layer. Eclipse itself is an optimistic rollup with a unique architecture; the platform acts as a dedicated settlement layer upon which execution rollup layers can be built. These execution layers are referred to as modular rollups or layer 3 networks. In doing so, Eclipse enables the deployment of completely modular architectures which separates the functions of consensus and data availability, settlement and execution into separate layers.
This approach to building rollups on completely modular architecture facilitates a greater degree of flexibility, specialisation and scalability than is possible for traditional rollups or monolithic architectures. Presently, the throughput of web2 infrastructure eclipses that of web3. For example, every second, roughly 40,000 Google searches are made, an impossible feat on a blockchain such as Ethereum with a transaction throughput of roughly 30 TPS. However, Eclipse offers rollups as a service, allowing developers to deploy application-specific rollups which can specialise in their intended purpose while retaining composability with a wider ecosystem. Consequently, Eclipse claims that its modular rollups can process up to 100,000 TPS, making it a viable web3 alternative for high throughput applications.
How Does Eclipse Work?
Eclipse is a platform for the deployment of modular rollups. Providing a flexible modular architecture, Eclipse allows developers to choose the virtual machine, settlement process, consensus and data availability layer that best suits their needs. Within this modular framework, the Eclipse network provides the settlement layer:
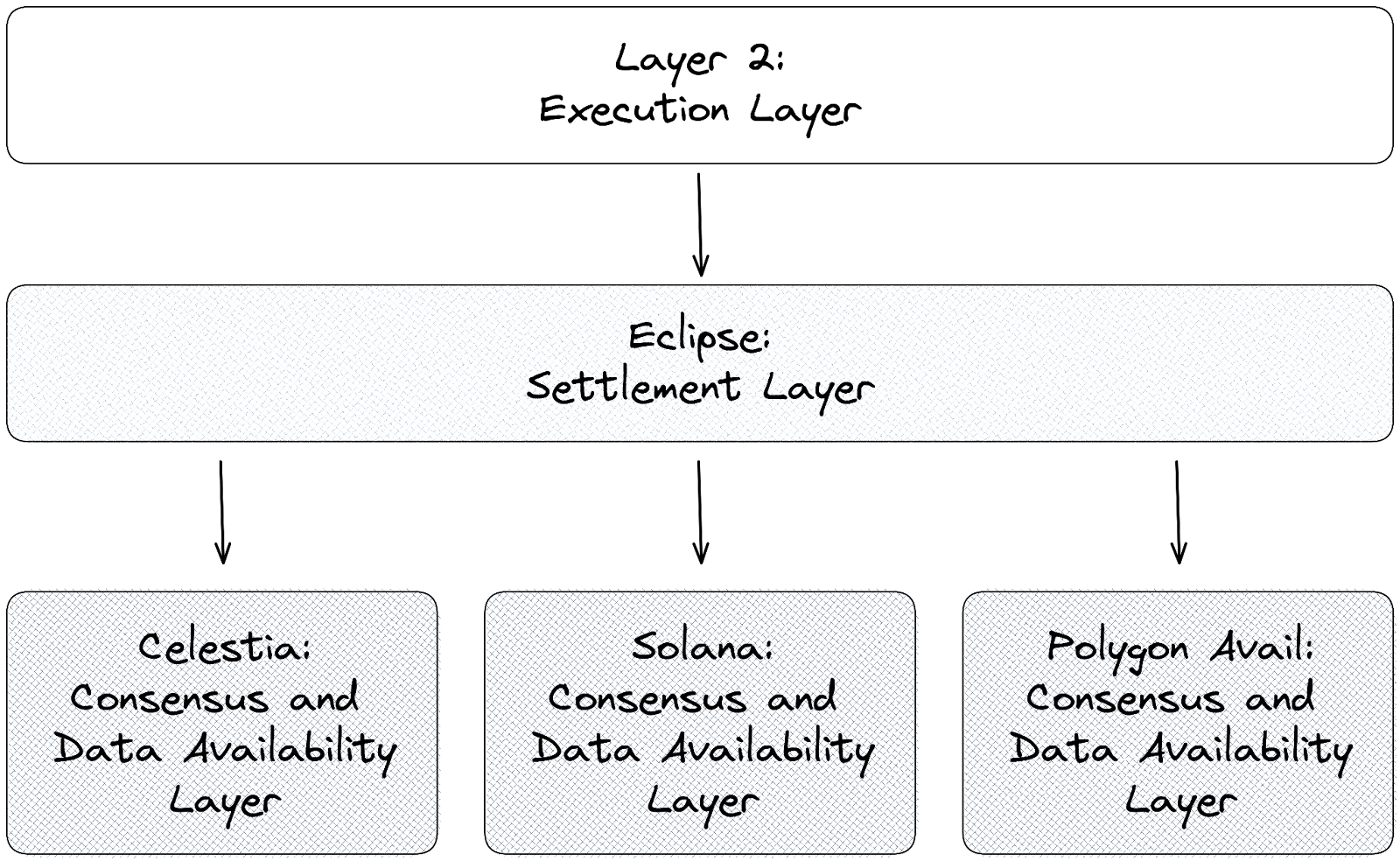
At the heart of each modular rollup is the virtual machine, responsible for executing transactions. The virtual machine is a critical component of any blockchain as it converts smart contract code written in high-level programming languages such as Solidity or Rust into bytecode that can be executed on the blockchain. To provide additional customisation and compatibility, Eclipse supports both the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM), with plans to add virtual machines in the future. By leveraging parallelism in the Eclipse virtual machine, its implementation of the EVM is ten times faster than Optimism.
The settlement process is a critical aspect of ensuring the correct execution of transactions. There are two forms of settlement on Eclipse: optimistic and zero-knowledge. The optimistic settlement allows the executor to specify the result for each block of transactions, and verifiers are responsible for challenging incorrect results. On the other hand, zero-knowledge settlement requires the executor to provide strong evidence that the result is correct. However, the mechanism behind settlement on Eclipse is what differentiates the protocol; Eclipse itself acts as the dedicated settlement layer for the modular architectures it takes part. Referred to as a settlement rollup, Eclipse handles the process of bridging and passing proofs without relying on a layer 1 blockchain. Presently, Eclipse offers an optimistic settlement and is working on a zero-knowledge virtual machine that will enable zero-knowledge proofs to be utilised in the settlement process.
Sharing a virtual machine with Ethereum or Solana greatly enhances the potential of Eclipse rollups. By leveraging existing tooling, such as smart contracts, the development of the ecosystem can be expedited, as they can be deployed without the need for additional steps or processes. Furthermore, the compatibility of wallets and block explorers with Ethereum or Solana means that modular rollups built using the same virtual machine will also be supported. This provides a seamless experience for users, further increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of the ecosystem.
Eclipse is dedicated to providing secure and efficient solutions for asset bridging between chains. As modular rollups may be application or sector-specific, bridging is crucial for the growth of ecosystems and fostering of the network effect. To achieve this, Eclipse intends to support the Hyperlane bridge and Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC). The Hyperlane bridge, being a full node solution, offers fast finality bridging by verifying the correctness of transactions independently. The IBC protocol, on the other hand, provides standard fast finality bridging between Eclipse chains, while non-Eclipse chains require a challenging period to ensure the validity of IBC messages. These protocols will together ensure seamless interoperability within the Eclipse ecosystem and with other networks.
Why Modularise Rollups?
Given the complexity associated with creating a framework for the deployment of rollups operating within a modular blockchain architecture, the question arises, why modularise rollups? Traditional rollups – implemented as layer 2 scaling solutions – already offer improved efficiency and flexibility. Additionally, they can be deployed as standalone smart contracts on a preferred base layer without requiring involvement from the Eclipse team to build using their development stack. Yet, despite these advantages, modular rollups offer a distinct set of benefits not found in either traditional rollups or current blockchain systems.
By modularising rollups, Eclipse enables a greater degree of efficiency than even exists in traditional rollups. The protocol leverages parallelism, the concept of executing multiple transactions simultaneously, which is why its implementation of the EVM is 10 times faster than Optimism, an ethereum rollup that can process roughly 2,000 transactions per second. Furthermore, leveraging the present data availability layers offered to builders through Eclipse lessens the costs of verifying and storing transaction data when compared to Ethereum, the predominant rollup base layer.
One specific area in which Eclipse stands out is the unparalleled flexibility and customization offered to builders creating modular rollups, beyond simply selecting a virtual machine for the rollup. By utilising modular rollups access to network infrastructure, smart contract deployment, and transactions can be restricted, allowing for the creation of regulatory-compliant chains. Block constraints can be enforced so that specific transactions are forced or negated within each block. Additionally, Eclipse supports the deployment of specialised opcodes, enabling unique operations within the virtual machine. Finally, gas fees can be subsidised, charged at cost, or set at a premium, and paid for using various currencies, not just the native currency of the rollup’s virtual machine.
Unlike traditional rollups, rollups built using Eclipse operate within a completely modular architecture. Separating the functions of data availability and consensus, settlement and execution into dedicated layers, Eclipse aims to achieve higher levels of efficiency and flexibility than is present on many monolithic blockchains. However, the possibilities of modular blockchains encompass more than efficiency and flexibility. Enabled by the addition of new components to the system as needed, Eclipse’s modular framework allows for a high degree of scalability. Furthermore, by splitting blockchain functions between networks, Eclipse offers a higher degree of decentralisation in the underlying layers than exists in rollups built on monolithic blockchains. Each individual module, being independent, makes it harder for a single point of weakness to compromise the totality of the network, enhancing its security.
The Future of Eclipse
Eclipse is implementing a number of improvements and solutions before launching its mainnet. However, Eclipse has launched multiple testnets, working with their private beta group to trial the technology. Over the coming months, Eclipse has announced plans to expand the testnet and begin offering their modular rollups to a larger number of users. This process will occur before launching the mainnet in order to test the network’s core features and ensure its functionality.
Toward the second half of 2023, Eclipse has announced plans to enable fraud proofs, allowing the network to function in its intended role as a settlement layer. It will begin bridging and passing proofs for the modular rollups launched on the Eclipse testnet. In the same timeframe, the network will begin to decentralise, a process that will likely involve dispersing the node set and opening access to stakeholders to participate in validation.
As Eclipse approaches the mainnet launch, the team has announced its commitment to accommodating user demands by incorporating alternative virtual machines and data availability layers. The highly anticipated Move virtual machine is expected to be among the additions, owing to its innovative parallel transaction execution capabilities and growing popularity. To date, Eclipse has already tested and supports several data availability layers, including Celestia, Polygon Avail, and EigenLayer. Additionally, as Ethereum moves toward the completion of its rollup-centric roadmap, improvements such as danksharding will pave the way for the network to be adopted by Eclipse as a data availability layer.
Gradually, as the Eclipse network moves toward completion, it will possess the requisite functionality to become the settlement layer for numerous modular rollups. Constructed using the powerful Cosmos infrastructure enables modular rollup networks to take advantage of interoperability not only within the Eclipse network but also throughout the expansive Cosmos ecosystem. This interoperability, facilitated by Cosmos, opens up the network effect to application-specific rollup networks, positioning Eclipse as a promising candidate to become a prominent base layer for rollup networks, emerging as the universal layer 2.
In trying to achieve this final destination, Eclipse has the potential to transform the blockchain landscape, delivering a highly scalable and composable platform that empowers developers to design custom modular rollups to meet their specific needs. With its customizability and compatibility, Eclipse provides the ideal environment for executing high-throughput Web3 applications in areas such as gaming and DeFi, overcoming the limitations of existing solutions such as a lack of flexibility or composability. General-purpose networks tend to lack the specialised solutions required for specific use cases, while application-specific networks often fall short in terms of interoperability and fail to harness the network effect. With its modular architecture, Eclipse offers a promising framework that may soon become the preferred platform for a diverse array of rollups, playing host to a thriving blockchain ecosystem.
Conclusion
Eclipse transforms the deployment of layer 3 networks with its cutting-edge modular rollup framework. As a sovereign settlement rollup, Eclipse is intended to serve as the facilitator for a thriving ecosystem of modular networks. The network provides a high degree of flexibility, with a variety of virtual machines and base layers for modular rollups to choose from. These characteristics, coupled with Eclipse’s IBC-enabled composability, make the network a desirable choice for any organisation looking to adopt a dedicated execution environment. With its vast potential, the Eclipse network has the capacity to evolve into a universal layer 2, becoming the ultimate hub for a modular blockchain ecosystem.
About Zerocap
Zerocap provides digital asset investment and digital asset custodial services to forward-thinking investors and institutions globally. For frictionless access to digital assets with industry-leading security, contact our team at hello@zerocap.com or visit our website www.zerocap.com
DISCLAIMER
Zerocap Pty Ltd carries out regulated and unregulated activities.
Spot crypto-asset services and products offered by Zerocap are not regulated by ASIC. Zerocap Pty Ltd is registered with AUSTRAC as a DCE (digital currency exchange) service provider (DCE100635539-001).
Regulated services and products include structured products (derivatives) and funds (managed investment schemes) are available to Wholesale Clients only as per Sections 761GA and 708(10) of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) (Sophisticated/Wholesale Client). To serve these products, Zerocap Pty Ltd is a Corporate Authorised Representative (CAR: 001289130) of AFSL 340799
All material in this website is intended for illustrative purposes and general information only. It does not constitute financial advice nor does it take into account your investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs. You should consider the information in light of your objectives, financial situation and needs before making any decision about whether to acquire or dispose of any digital asset. Investments in digital assets can be risky and you may lose your investment. Past performance is no indication of future performance.
FAQs
What is Eclipse and how does it relate to blockchain architecture?
Eclipse is a platform for the development of modular rollups, which are a type of layer 2 scaling solution that executes transactions off-chain before bundling them into a single transaction and executing them as a batch on the base layer. In the context of blockchain architecture, Eclipse acts as a dedicated settlement layer upon which execution rollup layers can be built. These execution layers are referred to as modular rollups or layer 3 networks. This approach enables the deployment of completely modular architectures which separates the functions of consensus and data availability, settlement and execution into separate layers.
How does Eclipse address the blockchain trilemma?
The blockchain trilemma refers to the challenge of achieving decentralisation, security, and scalability simultaneously in a blockchain system. Eclipse addresses this issue by leveraging blockchain modularity to maximise efficiency and flexibility. By separating the functions of consensus and data availability, settlement and execution into dedicated layers, Eclipse can achieve higher levels of efficiency and flexibility than is present in many monolithic blockchains.
What is the role of virtual machines in the Eclipse network?
Virtual machines are at the heart of each modular rollup in the Eclipse network, responsible for executing transactions. They convert smart contract code written in high-level programming languages such as Solidity or Rust into bytecode that can be executed on the blockchain. Eclipse supports both the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM), with plans to add more virtual machines in the future.
What is the future of Eclipse?
Eclipse is implementing a number of improvements and solutions before launching its mainnet. Over the coming months, Eclipse plans to expand the testnet and begin offering their modular rollups to a larger number of users. By the second half of 2023, Eclipse plans to enable fraud proofs, allowing the network to function in its intended role as a settlement layer. As the Eclipse network moves toward completion, it will possess the requisite functionality to become the settlement layer for numerous modular rollups, potentially emerging as the universal layer 2.
What are the benefits of Eclipse’s modular rollup framework?
Eclipse’s modular rollup framework offers a greater degree of efficiency and flexibility than traditional rollups or current blockchain systems. By leveraging parallelism, Eclipse’s implementation of the EVM is ten times faster than Optimism, an ethereum rollup that can process roughly 2,000 transactions per second. Furthermore, Eclipse’s modular framework allows for a high degree of scalability and a higher degree of decentralisation in the underlying layers than exists in rollups built on monolithic blockchains.
Like this article? Share
Latest Insights
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 21st July 2025
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 14th July 2025
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Zerocap selects Pier Two to offer institutional staking yields
Institutional clients gain secure, non-custodial access to native crypto yields with top-tier infrastructure Leading digital asset firm Zerocap has selected global institutional staking provider Pier
Receive Our Insights
Subscribe to receive our publications in newsletter format — the best way to stay informed about crypto asset market trends and topics.


 Share
Share  Tweet
Tweet  Post
Post 