Content
- What Are Decentralised Communication Protocols?
- Why Are Decentralised Communication Protocols Necessary For Blockchains?
- Decentralised Communication Protocols In Action
- Challenges And Limitations Of Decentralised Communication Protocols
- Conclusion
- About Zerocap
- DISCLAIMER
- FAQs
- What are Decentralised Communication Protocols in blockchain technology?
- What is the role of Decentralised Communication Protocols in achieving consensus in blockchain networks?
- What are some examples of Decentralised Communication Protocols used in blockchain networks?
- What are the challenges and limitations of Decentralised Communication Protocols?
- What is the future of Decentralised Communication Protocols in blockchain technology?
19 May, 23
The Role of Decentralised Communication in Blockchains

- What Are Decentralised Communication Protocols?
- Why Are Decentralised Communication Protocols Necessary For Blockchains?
- Decentralised Communication Protocols In Action
- Challenges And Limitations Of Decentralised Communication Protocols
- Conclusion
- About Zerocap
- DISCLAIMER
- FAQs
- What are Decentralised Communication Protocols in blockchain technology?
- What is the role of Decentralised Communication Protocols in achieving consensus in blockchain networks?
- What are some examples of Decentralised Communication Protocols used in blockchain networks?
- What are the challenges and limitations of Decentralised Communication Protocols?
- What is the future of Decentralised Communication Protocols in blockchain technology?
Blockchain nodes can be analogised to people talking in a crowd – without sufficient coordination, the message of each individual is lost within the cacophony of voices. To enable communication, blockchain networks utilise decentralised communication protocols, transforming the discordance of messages into an ordered discussion whereby information is efficiently and effectively distributed to their intended recipients. First developed before the introduction of the internet, decentralised communication protocols have matured over the preceding decades, ultimately becoming a foundational innovation for the creation of blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin. As a result, recent advancements in the field are empowering the development of a decentralised future.

What Are Decentralised Communication Protocols?
Traditionally, most web-based applications rely on a third-party intimidatory, usually a server, to facilitate communication between applications or devices. For example, were a user to send an email to another user, the communication is initiated by sending it to their outgoing mail server which then utilises a Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to send the email to the recipient’s incoming mail server. The recipient’s incoming mail server then stores the email until the recipient retrieves it using a Post Office Protocol (POP) or Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP). These protocols all rely on organisations such as internet or email service providers to host them, without which communication would be impossible. This approach necessitates a degree of centralisation that is antithetical to the philosophy of blockchain technology. Hence the development of decentralised communication protocols to enable peer-to-peer (P2P) messaging.
Decentralised communication protocols, commonly referred to as P2P, are systems that enable communication between individuals or devices without a trusted intermediary. They are designed to provide a more secure, private, and resilient alternative to centralised communication systems. In a decentralised system, each participant in the network has equal access to the communication infrastructure and can interact with others directly. One of the most common forms of decentralised communication protocol is the P2P framework, used for file sharing. In a P2P network, each user shares their files with others on the network, and can also download files from other users without a central server that controls the network.
To facilitate decentralised communication, network participants are required to operate as both the client and the server. Therefore, each participant on the network is responsible for processing and relaying messages, as well as verifying the integrity of those messages. Typically, as in traditional communication protocols, decentralised communication protocols utilise encryption to prevent unauthorised access to messages, as well as to prevent interception or modification of messages by third parties. Decentralised communication protocols can be implemented in a variety of ways such as federated networks, mesh networks, and peer-to-peer file-sharing systems. However, presently, the most prominent implementation of such technology is through blockchain networks.
Why Are Decentralised Communication Protocols Necessary For Blockchains?
The driving force behind the adoption of the technology has been a conviction in the promise of a more efficient and decentralised financial system, a belief rooted in the idea that individuals should retain greater control over their finances. Hence, blockchain technology is inherently tied to libertarian ideals. These ideals were championed by Satoshi Nakamoto during the creation of Bitcoin in 2009. Bitcoin was specifically designed to eliminate the need for an intermediary to authenticate transactions by ingraining the qualities of decentralisation, transparency and trustlessness into the architecture of the network. In doing so, the network would eliminate the need for an intermediary to authenticate transactions and correspondingly, the potential for censorship from a third party. These values, represented by the Bitcoin network have been in large part imprinted onto the blockchain landscape and are carried by its users.
Created in the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, the development of blockchain technology was influenced by the weaknesses exposed in the traditional financial system. The crisis was largely a result of misplaced trust in financial institutions. Consequently, trustlessness is arguably at the core of blockchain technology; this value can only be achieved by removing the need for a central trusted authority to maintain the integrity of the system. Hence, the importance of decentralisation within blockchains that allow multiple participants or nodes to operate independently and verify the integrity of one another. However, the operation of decentralised networks of nodes would be impossible without a framework for communication between one another that does not rely on a central intermediary.
To operate without relying on trust assumptions, blockchain nodes must continually achieve consensus with one another regarding the state of the network. Consensus itself refers to the process by which all nodes in the network agree on the current state of the blockchain. It is achieved via a consensus mechanism that ensures that all nodes on the network possess the same copy of the blockchain ledger, and that the ledger is updated in a secure and tamper-resistant manner. This way, network participants can verify the state of the network without having to trust any individual node, and rely on the principle of “don’t trust, verify”. Without a reliable and decentralised communication mechanism between nodes, messages required to achieve consensus would have to be sent through a centralised intermediary, creating opportunities for tampering and undermining the trustless nature of the network. By ensuring secure decentralised communication among nodes, blockchain networks can maintain their trustless nature, allowing them to operate with unparalleled security and transparency.
Moreover, before consensus is achieved, each block must be settled. Settlement refers to the process of verifying the validity of transactions in a block and adding the block to the blockchain. It is typically achieved via committees of nodes, which similarly to consensus, requires continual communication. Assuming the committee achieves consensus regarding the validity of the block, the block is then added to the blockchain and can be considered settled. In most blockchain networks, settlement is irreversible. Once a transaction has been settled, it cannot be reversed or modified without consensus from the rest of the network. Without a secure and efficient decentralised communication mechanism, a settlement could not be reliably achieved by committees. This may severely impact the validity of the blockchain ledger.
Libertarian values among the web3 user base make decentralisation, trustlessness, and transparency essential to their adoption. Among these, P2P messaging holds great significance, as it enables decentralised networks of nodes to communicate without compromising trustlessness. This would make the processes of consensus and settlement, which are essential for security, less reliable. Thus, decentralised communication protocols play a crucial role in ensuring that blockchain networks operate effectively.
Decentralised Communication Protocols In Action
There are several different types of decentralised communication protocols employed by blockchain networks. The primary role of these communication protocols is to ensure that messages reach their intended recipient. Furthermore, said protocols must ensure that the data is fully received in an interpretable format. Generally, they employ a set of messaging standards and communication logic to format and route messages.
Presently, the gossip protocol is one of the most commonly used decentralised communication protocols. In blockchain networks, each node maintains a copy of the network’s entire transaction history, referred to as a ledger, and needs to keep this ledger in sync with the rest of the network to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. Within this context, the gossip protocol is used to propagate new transactions and blocks throughout the network, ensuring that all nodes receive the same information and they can remain in sync. The gossip protocol works by broadcasting information to a few other nodes in the network each time the sender receives a new block or transaction. The recipient nodes then repeat this process until the message is sent to every node in the network, thus completing the dissemination of information. This creates a “gossip” effect, where the information spreads throughout the network until all nodes have received it. The gossip protocol is highly efficient, as it only requires a subset of nodes to receive the information before it can be propagated to the entire network.
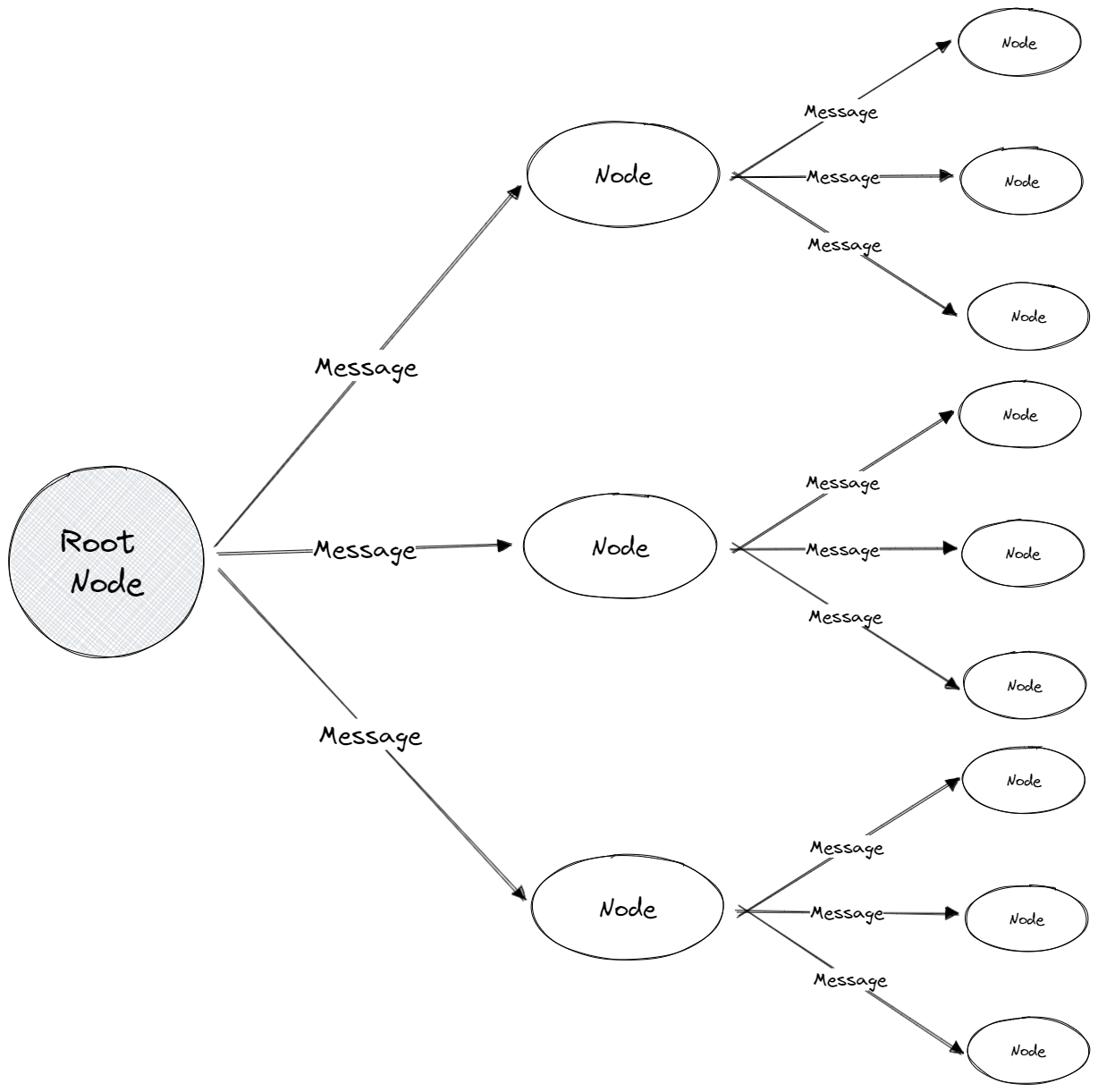
Another decentralised communication protocol utilised by blockchains is Kademlia. Employed by decentralised protocols such as IPFS, Kademlia is a distributed hash table that provides a framework for nodes to organise into a network and communicate with one another. Communication within Kademlia-based networks function via node lookups; the process of finding the location or address of a particular node or resource in the network. Communication itself occurs using User Datagram Protocol (UDP), a transport layer protocol in the Internet Protocol (IP) suite, which provides delivery of data between applications on a network. Each node is identified by a unique node ID and when a message is initiated, the Kademlia algorithm explores the network in a series of steps (the node lookup), contacting nodes that are progressively closer to the desired key until the value is found. The distributed hash table used for the node lookup is exhibited below;
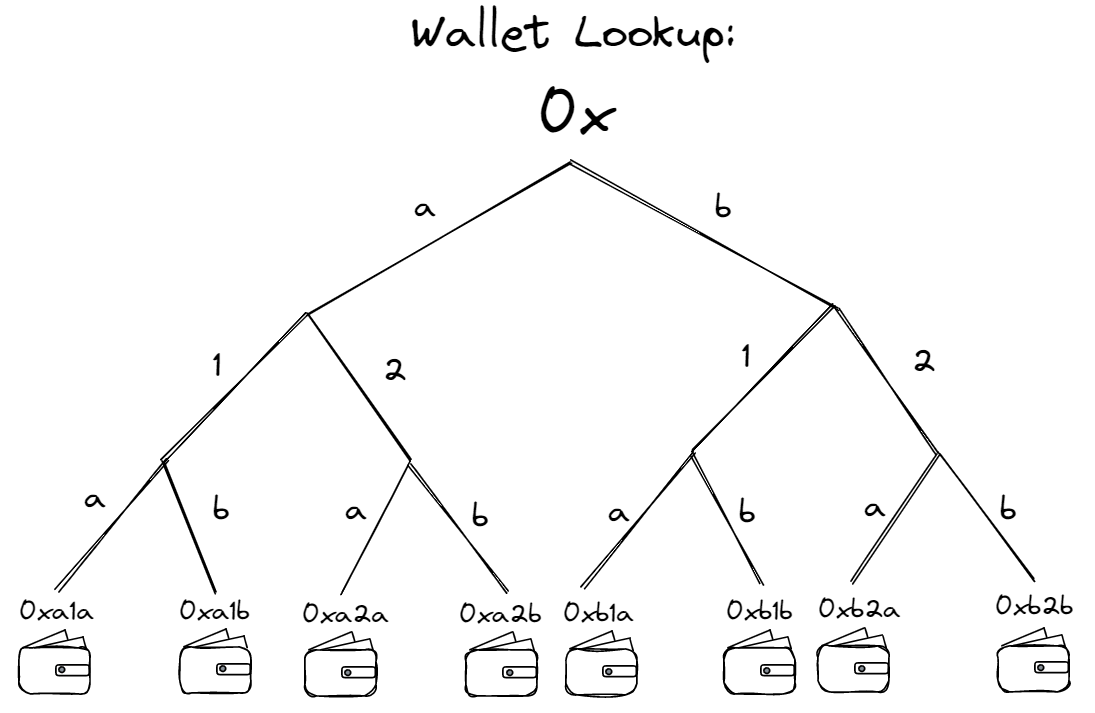
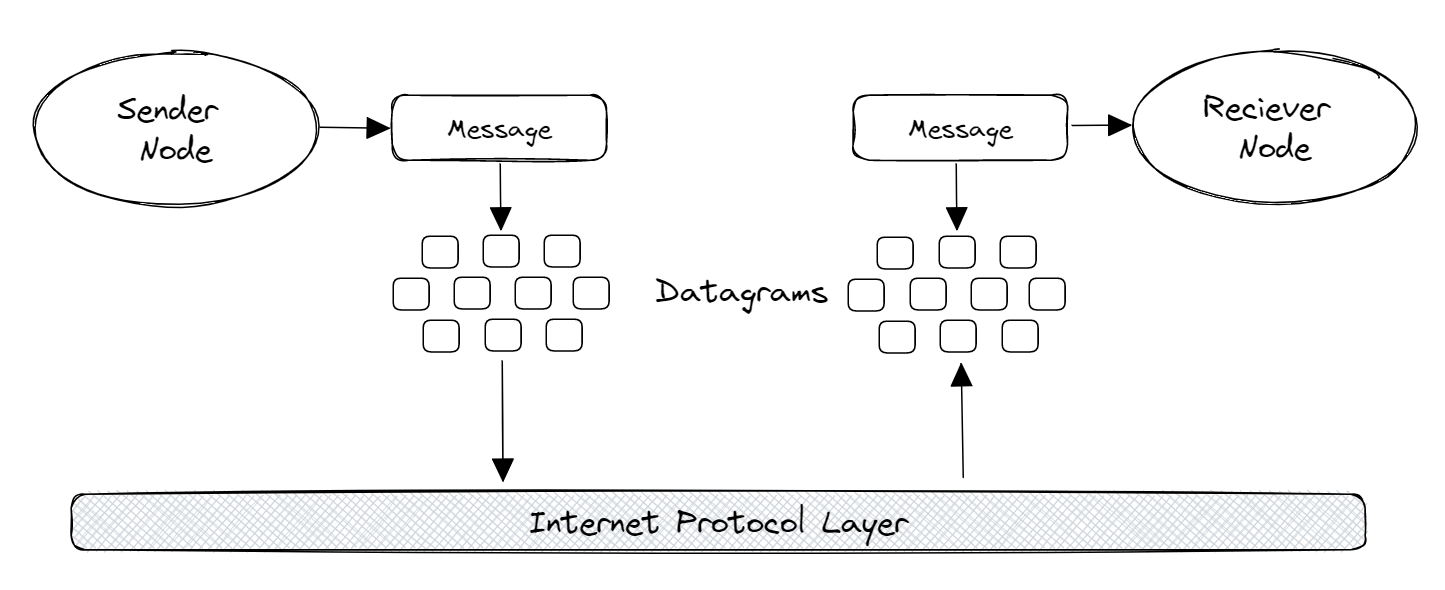
This process is highly efficient, as Kademlia only contacts a logarithmic number of nodes during the search. After the intended recipient is located using the Kademlia hash table, the message is sent via UDP. Using UDP, the message is broken into smaller packets referred to as datagrams containing a header that includes the source and destination port numbers, the length of the datagram, and a checksum for error detection. The datagrams are then sent to the Internet Protocol layer which routes datagrams to their destination based on the IP addresses of the source and destination hosts. Upon receipt of the datagrams, the receiving application uses the port number in the datagram header to identify the appropriate application to receive the message. The application then reassembles the datagrams into the original message and processes it.
Devp2p, Ethereum’s dedicated networking protocol, allows nodes to connect and communicate with each other over a decentralised network. It uses a system of discovery and routing to enable nodes to find and communicate with each other. Devp2p achieves this using a low-level communication layer that allows nodes to exchange messages directly. To facilitate reliable communication between nodes, Devp2p utilises a variety of mechanisms. Its peer discovery protocol uses a distributed hash table to store information about other available nodes, allowing them to connect with one another. Furthermore, messages are structured using a set of types that determine the message being sent. Lastly, Devp2p includes mechanisms for managing connections between nodes, including ping and pong messages to check the availability of peers. In addition to enabling basic communication between nodes, Devp2p can be used to build more complex protocols and services, such as the Whisper messaging protocol, which is built on top of Devp2p.
Separate from the intra-blockchain communication protocols discussed above is the inter-blockchain communication protocol, used to send and receive messages between blockchain networks rather than between nodes within a blockchain network. The concept of inter-blockchain communication introduces a number of challenges not encountered within intra-blockchain communication. These challenges primarily revolve around ensuring separate networks relying on different software, logic and even distinct codebases, can interpret messages sent between one another. However, the core philosophy remains consistent; to create a mechanism via which two separate parties can communicate without relying on a third party to relay the message.
Ultimately, these decentralised communication protocols serve as an algorithm to enable P2P messaging. Although Gossip, Kademlia and Devp2p are some of the most common decentralised communication protocols, many layer 1 blockchains utilise a custom protocol for inter-node communication. To obtain a requisite understanding of how said systems work, it is only necessary to recognise the mechanism by which network participants are identified and messages are propagated as this is the essence of how decentralised communication works.
Challenges And Limitations Of Decentralised Communication Protocols
Sending and receiving messages without a central authority to handle data poses several unique challenges. Since nodes act as both the client and server, they must handle a number of responsibilities that participants in a centralised network would not have to account for. Nodes are required to format and store data, propagate and verify messages, in addition to several other roles critical for the operation of a network. Creating an efficient and lightweight decentralised communication protocol to reduce the burden on nodes is where the challenge arises.
As blockchain networks scale, the necessity of fast communication increases. As the number of nodes in the network increases, so does the amount of communication required to maintain the network and achieve consensus. After all, consensus requires that all nodes in the network have access to the same information, meaning each newly settled block must be quickly disseminated to the entire network in order for security to be ensured. This can lead to increased latency and reduced throughput, making it more difficult for the network to operate effectively. Therefore, the importance of a decentralised communication protocol that can quickly spread large amounts of data to its intended receiver cannot be understated.
Furthermore, efficient decentralised communication is essential for maintaining the security of a network. In a proof-of-work system, for example, miners must compete to solve complex mathematical problems in order to add new blocks to the chain. The faster and more efficient the communication between miners, the higher the chances of successfully mining a block and earning the associated rewards. If communication is slow or inefficient, miners may waste computational resources on outdated block versions, leading to wasted time and energy.
Additionally, nodes within a blockchain network are required to maintain the health of the network. Specifically, they must ensure that it is running efficiently and effectively. This includes monitoring network performance, troubleshooting problems, and performing regular maintenance tasks. Nodes need to be able to detect any anomalies or irregularities in the network as soon as possible to prevent any potential disruptions or attacks. For example, if a node detects a sudden spike in network traffic, it may indicate a potential Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack, which could cause significant damage to the network. By having an efficient communication protocol in place, nodes can quickly share this information with other nodes, allowing them to take necessary measures to mitigate the attack. Similarly, regular maintenance tasks such as software updates are also necessary for keeping the network healthy. An efficient communication protocol enables nodes to efficiently share updates with one another, ensuring that all nodes are up to date and reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Decentralised communication protocols are crucial for the trustless operation of blockchain networks. Without these protocols, the client-server duality of blockchain nodes that allows them to operate on a trustless assumption would be impossible. Considering that these values are essential to the web3 user base, the decentralisation and trustlessness enabled by gossip, Kademlia, devp2p, and other communication protocols are essential for the adoption of web3 technology. While decentralised messaging poses challenges, it has the potential to transform the way we communicate, enabling interactions without impediment by intermediaries.
About Zerocap
Zerocap provides digital asset investment and digital asset custodial services to forward-thinking investors and institutions globally. For frictionless access to digital assets with industry-leading security, contact our team at [email protected] or visit our website www.zerocap.com
DISCLAIMER
Zerocap Pty Ltd carries out regulated and unregulated activities.
Spot crypto-asset services and products offered by Zerocap are not regulated by ASIC. Zerocap Pty Ltd is registered with AUSTRAC as a DCE (digital currency exchange) service provider (DCE100635539-001).
Regulated services and products include structured products (derivatives) and funds (managed investment schemes) are available to Wholesale Clients only as per Sections 761GA and 708(10) of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) (Sophisticated/Wholesale Client). To serve these products, Zerocap Pty Ltd is a Corporate Authorised Representative (CAR: 001289130) of AFSL 340799
All material in this website is intended for illustrative purposes and general information only. It does not constitute financial advice nor does it take into account your investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs. You should consider the information in light of your objectives, financial situation and needs before making any decision about whether to acquire or dispose of any digital asset. Investments in digital assets can be risky and you may lose your investment. Past performance is no indication of future performance.
FAQs
What are Decentralised Communication Protocols in blockchain technology?
Decentralised communication protocols, often referred to as peer-to-peer (P2P) systems, enable communication between individuals or devices without a trusted intermediary. They provide a more secure, private, and resilient alternative to centralised communication systems. In a decentralised system, each participant in the network has equal access to the communication infrastructure and can interact with others directly. These protocols are crucial for blockchain networks as they enable nodes to communicate and maintain the integrity of the network without relying on a central authority.
What is the role of Decentralised Communication Protocols in achieving consensus in blockchain networks?
Decentralised communication protocols play a crucial role in achieving consensus within blockchain networks. Consensus refers to the process by which all nodes in the network agree on the current state of the blockchain. It is achieved via a consensus mechanism that ensures all nodes on the network possess the same copy of the blockchain ledger, and that the ledger is updated in a secure and tamper-resistant manner. Without a reliable and decentralised communication mechanism between nodes, messages required to achieve consensus would have to be sent through a centralised intermediary, creating opportunities for tampering and undermining the trustless nature of the network.
What are some examples of Decentralised Communication Protocols used in blockchain networks?
There are several types of decentralised communication protocols employed by blockchain networks. The gossip protocol is one of the most commonly used, where each node broadcasts information to a few other nodes in the network each time it receives a new block or transaction. The recipient nodes then repeat this process until the message is sent to every node in the network. Another protocol is Kademlia, a distributed hash table that provides a framework for nodes to organise into a network and communicate with one another. Devp2p, Ethereum’s dedicated networking protocol, allows nodes to connect and communicate with each other over a decentralised network.
What are the challenges and limitations of Decentralised Communication Protocols?
Decentralised communication protocols face several challenges. As blockchain networks scale, the necessity of fast communication increases. As the number of nodes in the network increases, so does the amount of communication required to maintain the network and achieve consensus. This can lead to increased latency and reduced throughput, making it more difficult for the network to operate effectively. Additionally, nodes within a blockchain network are required to maintain the health of the network, which includes monitoring network performance, troubleshooting problems, and performing regular maintenance tasks. An efficient communication protocol enables nodes to efficiently share updates with one another, ensuring that all nodes are up to date and reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities.
What is the future of Decentralised Communication Protocols in blockchain technology?
The future of decentralised communication protocols in blockchain technology is promising. As the technology matures and more efficient protocols are developed, the speed and reliability of communication within blockchain networks are expected to improve. This will enable blockchain networks to scale more effectively and handle larger volumes of transactions. Furthermore, as the regulatory environment for blockchain technology becomes more clear, the adoption of decentralised communication protocols is likely to increase, further driving the development and innovation in this field.
Like this article? Share
Latest Insights
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 2 February 2026
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 19 January 2026
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 12 January 2026
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Receive Our Insights
Subscribe to receive our publications in newsletter format — the best way to stay informed about crypto asset market trends and topics.


 Share
Share  Tweet
Tweet  Post
Post 