Content
- What Is Avalanche?
- How Does Avalanche Work?
- Cultivating A Multichain Ecosystem
- Conclusion
- About Zerocap
- FAQs
- What is Avalanche and how does it work?
- What is the Avalanche Consensus?
- What are the key components of Avalanche's architecture?
- What are subnets in Avalanche?
- What is the Avalanche Multiverse?
- DISCLAIMER
6 Jun, 23
What is Avalanche?

- What Is Avalanche?
- How Does Avalanche Work?
- Cultivating A Multichain Ecosystem
- Conclusion
- About Zerocap
- FAQs
- What is Avalanche and how does it work?
- What is the Avalanche Consensus?
- What are the key components of Avalanche's architecture?
- What are subnets in Avalanche?
- What is the Avalanche Multiverse?
- DISCLAIMER
Within the arena of blockchain technology, the battle to become the preeminent smart contract platform has seen Avalanche rise to prominence. The platform’s success can be largely attributed to its optimisations of integral blockchain characteristics, with the intent to accommodate a system at the scale of global finance. Avalanche has also overseen the introduction of several innovations such as the instantiation of multiple virtual machines, the implementation of its own novel consensus algorithm and most notably the network’s recent move to become a multichain ecosystem. Thus, in this coliseum of intense competition Avalanche appears poised to rise to preeminence, leading a multichain army.

What Is Avalanche?
Avalanche is an open-source platform designed for the development of decentralised applications (DApps) within an interoperable, highly scalable ecosystem. As one of the first ecosystems specifically designed to accommodate the demands of global finance, Avalanche delivers near-instant transaction finality with less than 2 seconds for transaction settlement. The rapid finality time is enabled by the platform’s cutting-edge consensus algorithm which also delivers strong security guarantees, with an 80% centralisation threshold as well as high throughput without sacrificing decentralisation, among other things. Situated as a forerunner in the crypto landscape, Avalanche uses Proof of Stake (PoS) as its consensus mechanism, making it an energy-efficient and sustainable choice compared to blockchains utilising Proof of Work (PoW) based consensus.
Avalanche distinguishes itself from other blockchain platforms in various ways, with its consensus protocol being one of the most significant factors. Avalanche’s novel consensus mechanism, the Avalanche Consensus, offers a unique blend of scalability, speed, and decentralisation. Unlike traditional PoW or PoS systems, Avalanche consensus is built upon a groundbreaking approach known as Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) optimization. This enables the platform to achieve high throughput, supporting more than 4,500 transactions per second (TPS), and finality in mere seconds. Additionally, Avalanche’s design accommodates developers by offering compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and a variety of programming languages, including Solidity, Rust, and Go. This compatibility enables seamless migration of DApps and assets from Ethereum to Avalanche, helping foster the network effect.
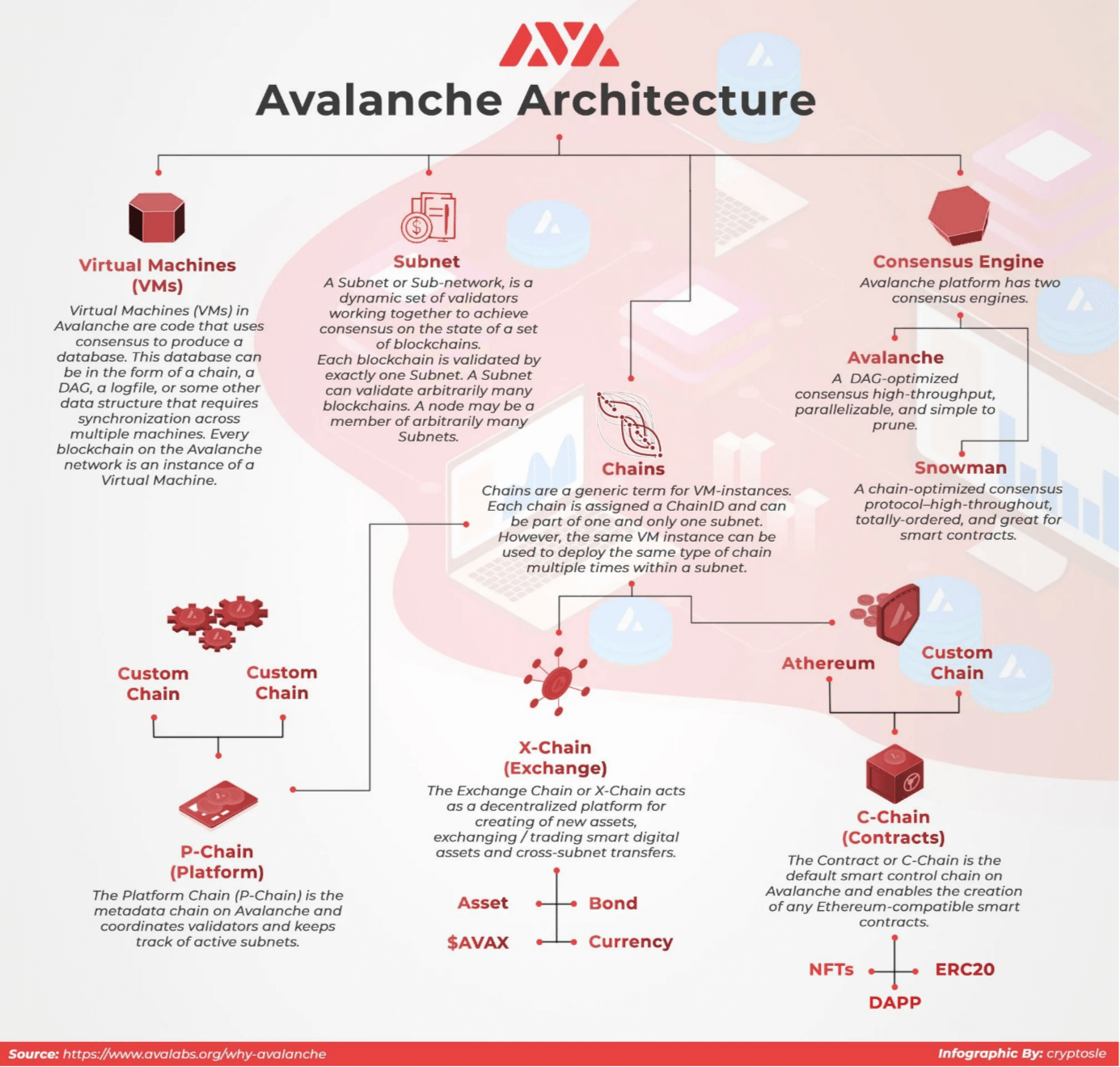
Diving deeper into Avalanche’s architecture, the platform consists of multiple dynamic and interconnected blockchains. Together, these blockchains make up the Avalanche protocol. Avalanche itself, referred to as the Primary Network is a specialised subnet that hosts all of the network’s validators which validate the other blockchains. In addition to the Primary Network, Avalanche is built upon the Platform Chain (P-Chain), the Exchange Chain (X-Chain), and the Contract Chain (C-Chain). The P-Chain manages the platform’s validators, delegation, and subnet creation, while the X-Chain is responsible for handling asset creation, trading, and management. The C-Chain, on the other hand, focuses on smart contract execution and DApp deployment. Assets can be seamlessly transferred between these chains using atomic transactions, meaning transactions that are indivisible, either being completed fully or not at all. This design approach negates the necessity of compromises encountered by monolithic blockchains, thereby mitigating the issues of network congestion and high gas fees – an issue commonly experienced on other blockchain platforms. Moreover, Avalanche’s architecture also ensures that each chain can be upgraded or modified independently without affecting the entire network, providing a future-proof foundation for continuous development and innovation.
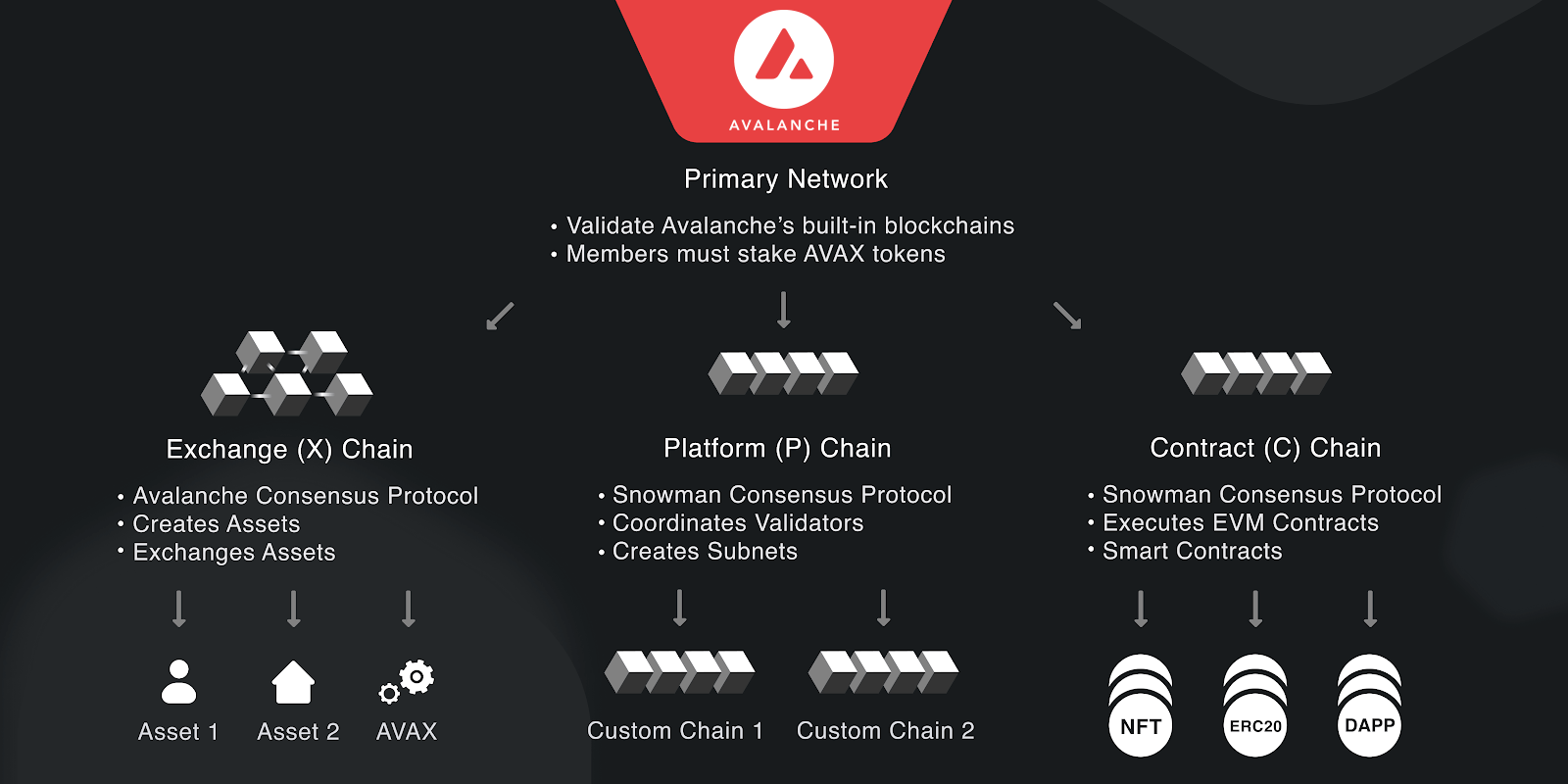
Source: Docs
What sets Avalanche apart from other blockchains is its innovative approach to scaling and flexibility. It achieves this through the implementation of Subnets, or subsets of the Avalanche Primary Network, that validate specific sets of blockchains. Avalanche’s subnets play a crucial role in creating a thriving, multichain ecosystem. Subnets are sovereign networks comprised of a subset of Avalanche validators, each of which can define its own execution logic, maintain its own state, manage its own security, and facilitate its own networking. This allows for a high degree of customisation and flexibility. In an effort to accelerate the adoption and growth of its novel subnet functionality, the Avalanche Foundation has launched the Avalanche Multiverse, an incentive program of up to US $290 million (up to 4 million AVAX) aimed at supporting new ecosystems such as gaming, DeFi, NFTs, and institutional use cases. This initiative is set to revolutionise the way developers and users interact with the blockchain, further solidifying Avalanche’s position as a leading player in the crypto world.
How Does Avalanche Work?
The Avalanche platform’s core consensus protocol, introduced in the ‘Scalable and Probabilistic Leaderless BFT Consensus through Metastability’ whitepaper, is a probabilistic Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) mechanism that does not require a designated leader or committee to achieve consensus. This leaderless approach allows the Avalanche network to scale effectively, accommodating millions of nodes while maintaining low latency and energy efficiency. The Avalanche consensus mechanism is built on repeated random subsampling, where nodes query a random set of peers to determine the state of the network. By leveraging the metastability properties of the protocol, the network can quickly reach a consensus on transactions with high probability. The consensus mechanism is robust against powerful adversaries, and it provides strong security guarantees even in the presence of sophisticated attackers.
The blockchain structure in Avalanche is based on a DAG, enhancing scalability and ensuring that transactions are processed quickly and efficiently. Unlike traditional blockchains that rely on a linear chain of blocks, the DAG structure in Avalanche allows for parallel transaction processing, greatly reducing confirmation times and increasing throughput. Furthermore, the DAG structure enables pruning, a process that eliminates the need to store the entire history of transactions, allowing the platform to grow sustainably over time. In the family of consensus protocols used by Avalanche, referred to as the Snow family, nodes can discard parts of the DAG that are deep and highly committed, as they do not need to prove past history to new bootstrapping nodes. This results in a more sustainable and efficient storage approach compared to blockchains based on the Nakamoto consensus.
Avalanche’s subnetworks, dubbed subnets, play a key role in its sharding capabilities that contribute to the platform’s overall performance and efficiency. Sharding is a technique that partitions system resources to increase performance and reduce load. In the context of Avalanche, network sharding is implemented through the creation of separate subnets that can operate independently and in parallel, reducing algorithmic load. State sharding and transaction sharding, which involve storing and maintaining specific subparts of the global state and processing incoming transactions separately, can also be implemented in Avalanche. Subnets are customised chains tailored to specific use cases or industries. These subnets can coexist and interact only when necessary, such as when a user wishes to perform an atomic swap between two subnets, reducing network congestion and increasing overall efficiency.
Governance in the Avalanche platform is facilitated through the use of its native token, AVAX, which enables on-chain governance for critical network parameters. Users can vote on changes and make decisions in a democratic manner, allowing for the adjustment of parameters such as the minimum staking amount, minting rate, and transaction fees. This empowers the platform to dynamically adapt and optimise its parameters through a crowd oracle. However, to ensure predictability and safety, Avalanche’s governance system imposes limits and time bounds on parameter changes, preventing drastic modifications in the short term while maintaining flexibility for long-term evolution. Governance in AVAX employs the concept of hysteresis, creating a dependency between recent parameter changes and the possibility of future adjustments. This design ensures that immediate and drastic changes to Avalanche are challenging to implement, promoting stability within the network. These constraints are eased as more time passes since the last change, ensuring that the system remains predictable over short time ranges and providing strong control as well as flexibility for the long term.
The Avalanche network itself is built upon the synergy between the consensus engine, the platform’s virtual machines, the three blockchains that make up the core Avalanche protocol and the subnets. The three Avalanche chains, X-Chain, P-Chain, and C-Chain, hosted and validated by the Primary Network, form the core of the Avalanche network:
- The X-Chain is designed to facilitate the creation and trading of smart assets, employing the Avalanche Consensus algorithm for fast finality and low fees. Transactions on the X-Chain use an unspent transaction output (UTXO) model, and fees are determined by a predefined fee schedule. The P-Chain, on the other hand, is responsible for coordinating validators and managing subnets. It uses a modified version of Avalanche Consensus, called Snowman, which linearizes the consensus process to ensure a clear history of events and total ordering. Like the X-Chain, the P-Chain also uses a UTXO transaction model and the same fee schedule. The C-Chain serves as an instance of the EVM, closely following the EVM architecture. It runs coreth, a Geth fork that leverages Snowman Consensus to produce a linear, totally ordered blockchain.
- The C-Chain adopts the account model for transactions and bases fees on EIP-1559. By integrating these components, Avalanche offers an efficient, secure, and adaptable ecosystem, enabling smooth interaction between various subnets, chains, and virtual machine (VM) instances to cater to diverse applications and use cases.
Source: https://twitter.com/MrFreshTime/status/1295485527114874883
Cultivating A Multichain Ecosystem
Avalanche Warp Messaging (AWM) serves as the cornerstone of Avalanche’s emerging multichain ecosystem, dubbed the multiverse. It is designed to facilitate communication across multiple subnets and foster an interconnected environment for cross-chain collaboration. AWM employs a hierarchical approach, with subnet-level nodes operating as message brokers for the platform. These message brokers follow a publish-subscribe pattern, where messages are published to specific channels, and subscribers receive updates relevant to their particular interests from the designated channels. By adopting a Merkle tree-based approach, the message brokers enable efficient message authentication, ensuring both data integrity and delivery. Additionally, AWM utilises Boneh-Lynn-Shacham (BLS) multi-signatures. A BLS multi-signature is a cryptographic scheme that enables multiple parties to collectively produce a single compact signature, which can be efficiently verified using their public keys. Utilising BLS enables the AWM to allow groups of validators to sign messages collectively with a single signature, which can be verified by anyone possessing the validators’ public keys. This powerful messaging system allows for greater fluidity and composability between Avalanche’s subnets, creating a foundation for multichain interactions.
By leveraging the potential of AWM, various applications and platforms can benefit from the inherent cross-chain communication capabilities. DeFi protocols can use AWM to exchange tokens and data between subnets, creating more diverse and liquid markets for users. Gaming platforms can develop cross-game assets and experiences that span multiple subnets, thereby enhancing the wider gaming landscape. Enterprise deployments can use AWM to facilitate information and transaction sharing between distinct permissioned subnets. Meanwhile, social networks and data providers can establish decentralised identity and reputation systems or offer data feeds and oracles to subnets in need of these services.
The recent Cortina network upgrade plays an essential role in cultivating the Avalanche multiverse, introducing significant improvements to the X-Chain and protocol optimizations. By migrating the X-Chain to the Snowman consensus and adopting a linear chain of blocks structure, Cortina enables a range of integrations, including AWM, complex transactions, state syncing, and broad exchange support. The upgrade also introduces a new network topology that reduces the number of hops required for messages to traverse the network, optimising communication between subnets and validators. Additionally, Cortina enhances the platform’s virtual machine capabilities, allowing for the efficient execution of custom smart contracts and DApps across subnets. These improvements are designed to ensure that the X-Chain can support an ecosystem of subnets.
The Avalanche multiverse, as it continues to expand, will unlock a number of opportunities for developers, businesses, and end-users alike. By enabling the deployment of an array of subnets, tailored to specific use cases, Avalanche is facilitating an environment suited toward the cultivation of an ecosystem of application-specific blockchains. App chains that exist in the siloed blockchain landscape typically face liquidity constraints and difficulty cultivating the network effect, a phenomenon whereby the value of a product increases as more people use it. Within the Avalanche multiverse, subnets will be able to grow and interact with one another, sharing users and liquidity, enabling the cultivation of the network effect. This may lead to new synergies, ultimately benefiting the end users who will enjoy access to an array of decentralised services and applications delivered by specialised networks.
Conclusion
Avalanche has emerged into the blockchain landscape as a part of the new wave, capitalising on the transpiration of new technologies and integrating them into a cohesive network. Its groundbreaking consensus algorithm and unique approach to multichain architecture have set the stage for a thriving ecosystem that caters to diverse use cases and industries. This commitment to continuous innovation, interoperability, and scalability will play a key role in the future of Avalanche, enhancing the way in which developers and users interact with the platform. With the continuous expansion of its multichain ecosystem, Avalanche is poised to rise as an industry leader, playing a pivotal role in the future of decentralised finance and blockchain technology.
About Zerocap
Zerocap provides digital asset liquidity and custodial services to forward-thinking investors and institutions globally. For frictionless access to digital assets with industry-leading security, contact our team at [email protected] or visit our website www.zerocap.com
FAQs
What is Avalanche and how does it work?
Avalanche is an open-source platform designed for the development of decentralised applications (DApps) within an interoperable, highly scalable ecosystem. It is designed to accommodate the demands of global finance, delivering near-instant transaction finality with less than 2 seconds for transaction settlement. Avalanche uses a unique consensus mechanism, the Avalanche Consensus, which offers a blend of scalability, speed, and decentralisation. It also supports more than 4,500 transactions per second (TPS), and finality in mere seconds. Avalanche’s architecture consists of multiple dynamic and interconnected blockchains, including the Platform Chain (P-Chain), the Exchange Chain (X-Chain), and the Contract Chain (C-Chain).
What is the Avalanche Consensus?
The Avalanche Consensus is a novel consensus mechanism that offers a unique blend of scalability, speed, and decentralisation. Unlike traditional Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) systems, Avalanche consensus is built upon a groundbreaking approach known as Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) optimization. This enables the platform to achieve high throughput, supporting more than 4,500 transactions per second (TPS), and finality in mere seconds.
What are the key components of Avalanche’s architecture?
Avalanche’s architecture consists of multiple dynamic and interconnected blockchains, which together make up the Avalanche protocol. These include the Platform Chain (P-Chain), the Exchange Chain (X-Chain), and the Contract Chain (C-Chain). The P-Chain manages the platform’s validators, delegation, and subnet creation, while the X-Chain is responsible for handling asset creation, trading, and management. The C-Chain focuses on smart contract execution and DApp deployment. Assets can be seamlessly transferred between these chains using atomic transactions.
What are subnets in Avalanche?
Subnets, or subsets of the Avalanche Primary Network, validate specific sets of blockchains. They play a crucial role in creating a thriving, multichain ecosystem. Subnets are sovereign networks comprised of a subset of Avalanche validators, each of which can define its own execution logic, maintain its own state, manage its own security, and facilitate its own networking. This allows for a high degree of customisation and flexibility.
What is the Avalanche Multiverse?
The Avalanche Multiverse is an incentive program launched by the Avalanche Foundation to accelerate the adoption and growth of its novel subnet functionality. The program, which offers up to US $290 million (up to 4 million AVAX), is aimed at supporting new ecosystems such as gaming, DeFi, NFTs, and institutional use cases. This initiative is set to revolutionise the way developers and users interact with the blockchain, further solidifying Avalanche’s position as a leading player in the crypto world.
DISCLAIMER
Zerocap Pty Ltd carries out regulated and unregulated activities.
Spot crypto-asset services and products offered by Zerocap are not regulated by ASIC. Zerocap Pty Ltd is registered with AUSTRAC as a DCE (digital currency exchange) service provider (DCE100635539-001).
Regulated services and products include structured products (derivatives) and funds (managed investment schemes) are available to Wholesale Clients only as per Sections 761GA and 708(10) of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) (Sophisticated/Wholesale Client). To serve these products, Zerocap Pty Ltd is a Corporate Authorised Representative (CAR: 001289130) of AFSL 340799
All material in this website is intended for illustrative purposes and general information only. It does not constitute financial advice nor does it take into account your investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs. You should consider the information in light of your objectives, financial situation and needs before making any decision about whether to acquire or dispose of any digital asset. Investments in digital assets can be risky and you may lose your investment. Past performance is no indication of future performance.
Like this article? Share
Latest Insights
Interview with Ausbiz: How Trump’s Potential Presidency Could Shape the Crypto Market
Read more in a recent interview with Jon de Wet, CIO of Zerocap, on Ausbiz TV. 23 July 2024: The crypto market has always been
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap, 22nd July 2024
Download the PDF Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact
What are Crypto OTC Desks and Why Should I Use One?
Cryptocurrencies have gained massive popularity over the past decade, attracting individual and institutional investors, leading to the emergence of various trading platforms and services, including
Receive Our Insights
Subscribe to receive our publications in newsletter format — the best way to stay informed about crypto asset market trends and topics.



 Share
Share  Tweet
Tweet  Post
Post 