Content
- What is a DEX?
- What is Uniswap?
- Uniswap V1
- Uniswap V2
- Conclusion
- About Zerocap
- FAQs
- What is Uniswap and how does it differ from traditional exchanges?
- What are the key differences between Uniswap V1 and V2?
- What is an Automated Market Maker (AMM) in the context of Uniswap?
- What are the benefits of using Uniswap's Decentralized Exchange?
- What are flash swaps and how do they work in Uniswap V2?
- DISCLAIMER
6 Jun, 23
Uniswap: Delving into V1 and V2

- What is a DEX?
- What is Uniswap?
- Uniswap V1
- Uniswap V2
- Conclusion
- About Zerocap
- FAQs
- What is Uniswap and how does it differ from traditional exchanges?
- What are the key differences between Uniswap V1 and V2?
- What is an Automated Market Maker (AMM) in the context of Uniswap?
- What are the benefits of using Uniswap's Decentralized Exchange?
- What are flash swaps and how do they work in Uniswap V2?
- DISCLAIMER
Uniswap’s origins lie in the foundation of decentralised exchange technology, emerging as a potent alternative to its centralised counterparts. Gaining prominence for its innovative approach to overcoming the limitations associated with centralised exchanges, Uniswap has been propelled to the forefront of DeFi. With each subsequent version, Uniswap has introduced cutting-edge features designed to address the complex and evolving needs of the rapidly growing DeFi community. Through continuous refinement and innovation, Uniswap has solidified its position as a leader in the DEX space, driving greater financial inclusion and democratising access to digital assets.

What is a DEX?
Decentralised exchanges, or DEXs, have emerged as a transformative force within the realm of digital asset trading, offering an alternative to the traditional centralised exchange model. Centralised exchanges have long been the predominant method for trading cryptocurrencies, with well-known platforms such as Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken serving millions of users worldwide. However, these centralised platforms come with their own set of limitations and risks, including the potential for hacks, downtime, and regulatory challenges.
In contrast, DEXs aim to address these concerns by leveraging the power of blockchain technology and smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer trading of digital assets, effectively removing the need for a centralised intermediary. This innovative approach enables users to retain full control of their funds, ensuring that they are not exposed to the vulnerabilities associated with centralised custodial solutions. Moreover, DEXs typically provide users with greater privacy, as there is no need to complete the often extensive Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures required by their centralised counterparts.
At their core, DEXs operate by leveraging smart contracts to automate the trading process, providing a secure, transparent, and decentralised environment for users to transact. Two primary models have emerged within the DEX landscape: order book-based DEXs and those utilising automated market makers (AMMs). Both models serve to facilitate peer-to-peer trading; however, they differ in their approach to matching buyers and sellers and determining asset prices. In an order book (OB) DEX, users make trades by submitting their order to the smart contract, specifying the desired trading pair and the amount they wish to trade. The smart contract then searches for a matching order on the platform’s order book, and once it identifies a suitable counterparty, the trade is executed automatically without the need for any human intervention.
Additionally, the majority of DEXs employ an AMM model, hence do not rely on an order book to match buyers and sellers. Instead, they utilise liquidity pools that act as collections of assets supplied by users known as liquidity providers. These pools are governed by smart contracts that automatically execute trades based on predefined algorithms. When a user wants to make a trade, they interact directly with the smart contract, which calculates the price of the assets being exchanged based on the current state of the liquidity pool.
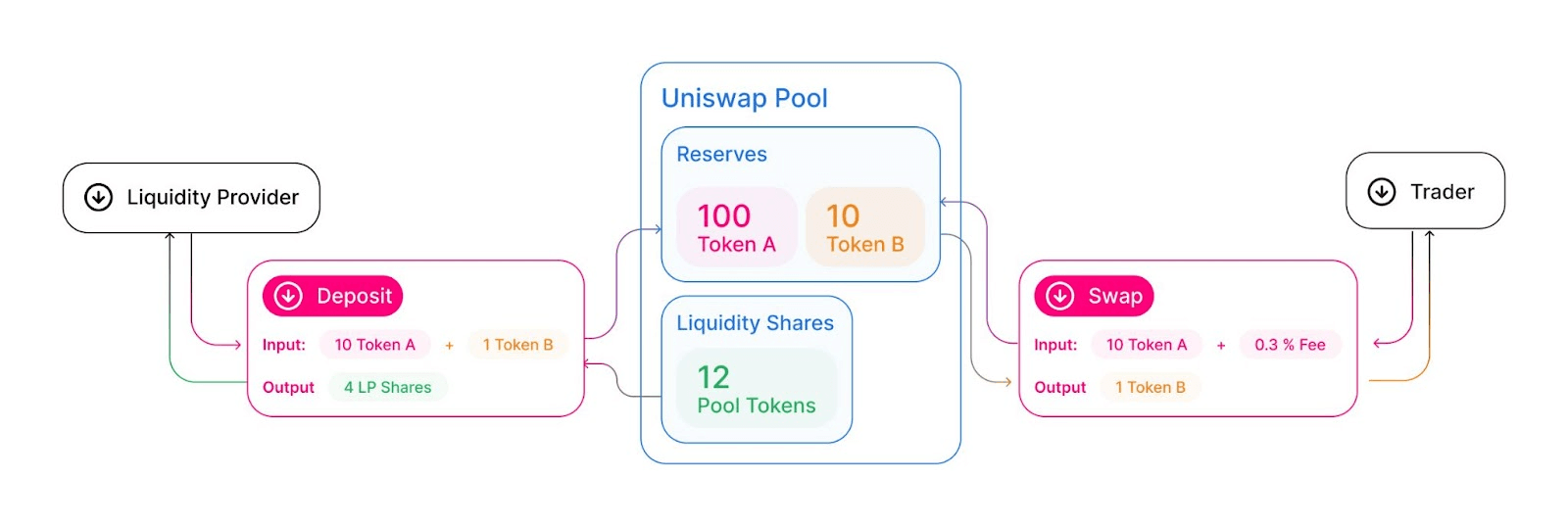
Source: Docs
Both the OB and AMM models have their own unique advantages, with the former offering more precise control over trade execution and the latter delivering a seamless experience without the need for order matching. However, several factors have caused the AMM model to become the preeminent structure for DEXs, including Uniswap. Ultimately, the choice between these models depends on the specific needs and preferences of the users and the broader goals of the DEX platform.
The growing prominence of DEXs can be attributed to several key factors, including their potential to drive greater financial inclusion, enhance security, and promote innovation within the blockchain ecosystem. By providing users with a means to transact directly with each other without the need for a centralised intermediary, DEXs can help to democratise access to financial services, particularly in geographical regions where traditional banking infrastructure may be limited or nonexistent.
Moreover, the decentralised and smart contract-based nature of DEXs mitigates the risk of hacks and security breaches that occur due to human participation. While DEXs can still encounter targeted attacks via smart contract vulnerabilities, the human error and single points of failure that plague centralised exchanges are absent. This enhanced security can provide users with greater peace of mind when trading and storing their digital assets. Furthermore, DEXs are often at the forefront of innovation in the blockchain space, with many platforms integrating cutting-edge features such as cross-chain compatibility, layer 2 scaling solutions, and advanced trading tools. As a result, DEXs have the potential to drive significant growth and development within the digital asset ecosystem, contributing to the ongoing maturation of the blockchain industry as a whole.
What is Uniswap?
Uniswap, a prominent player in the world of DeFi, is a DEX protocol built on Ethereum. It allows users to trade a variety of ERC-20 tokens without the need for a central authority, thereby providing a novel solution for the challenges faced by traditional, centralised exchanges. Uniswap’s prominence lies in its innovative use of AMMs to facilitate trades, eliminating the need for OBs and counterparty matching via market making firms. Nevertheless, each new release from Uniswap heralds the introduction of new features to address emerging market problems and improve the protocol as a whole.
Uniswap V1
Uniswap V1, the inaugural version of the protocol, was launched in November 2018 by developer Hayden Adams. It was conceived as a response to the prevailing liquidity and efficiency predicaments that plagued DEXs of the era. The groundbreaking platform harnessed the power of AMMs, a pioneering concept that set it apart from its contemporaries. Uniswap V1’s innovative approach eschewed the traditional OB model in favour of the now widely adopted liquidity pool system. Liquidity providers (LPs) were incentivised to deposit their assets into these pools, earning a share of the trading fees generated by the specific pool itself. This mutually beneficial arrangement not only stimulated liquidity within the ecosystem but also fostered a dynamic and self-sustaining environment, elevating the Uniswap V1 protocol to new heights within the rapidly expanding DeFi space.
At its core, Uniswap V1 employed an elegantly simple x * y = k formula, wherein x and y represented the quantities of two distinct tokens in a liquidity pool, and k functioned as a constant value. This formula allowed the protocol to autonomously calculate token prices and facilitate trades in a decentralised manner.
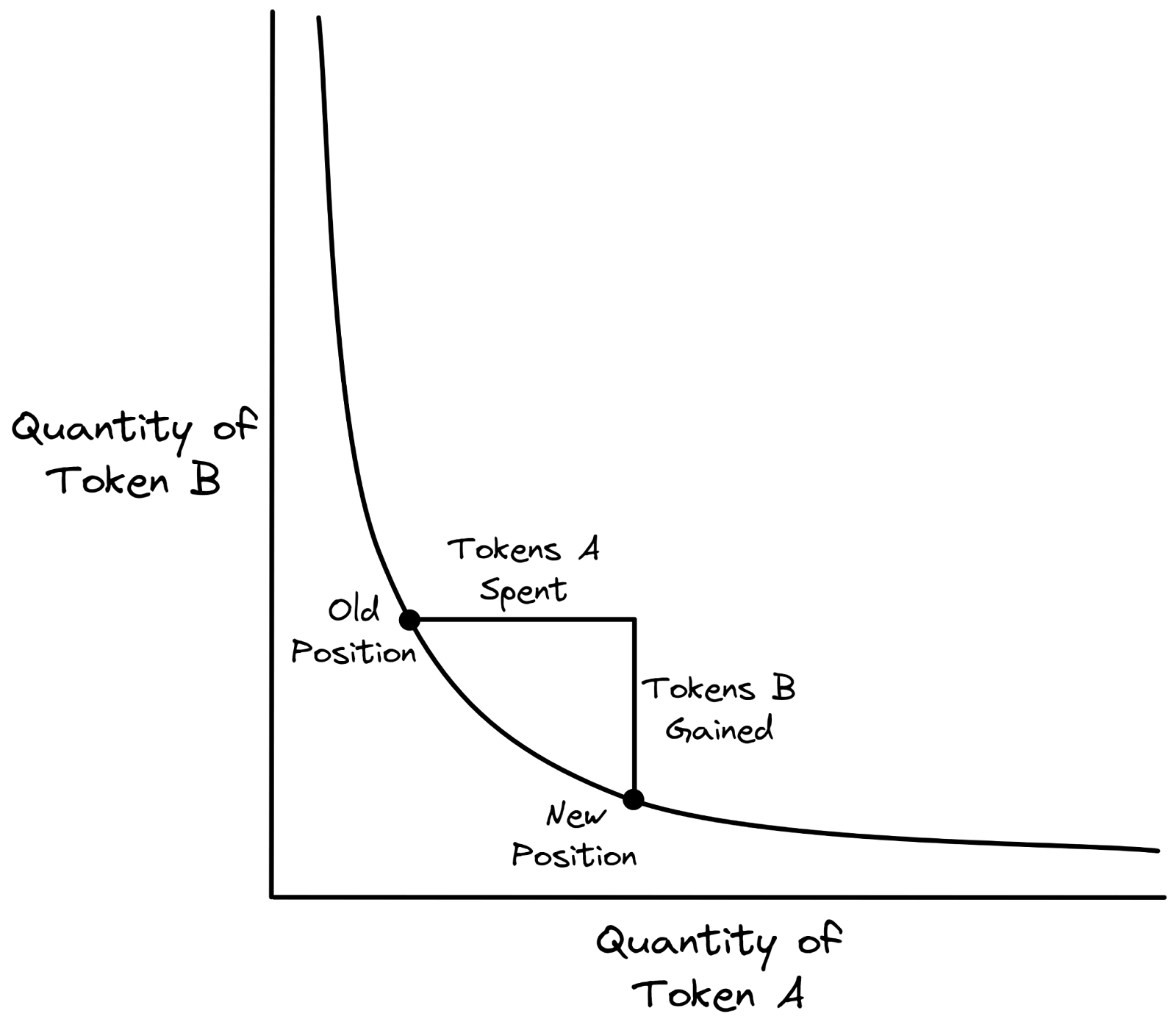
Nevertheless, despite its novel methodology, Uniswap V1 grappled with a number of limitations that constrained its full potential. One such constraint was its exclusive support for ERC-20/ETH trading pairs, effectively meaning that users who sought to trade between two different ERC-20 tokens were compelled to undertake an additional conversion step, first exchanging one token for ETH and subsequently converting the acquired ETH into the desired token. This process not only hampered overall efficiency but also led to an escalation in transaction costs for end-users.
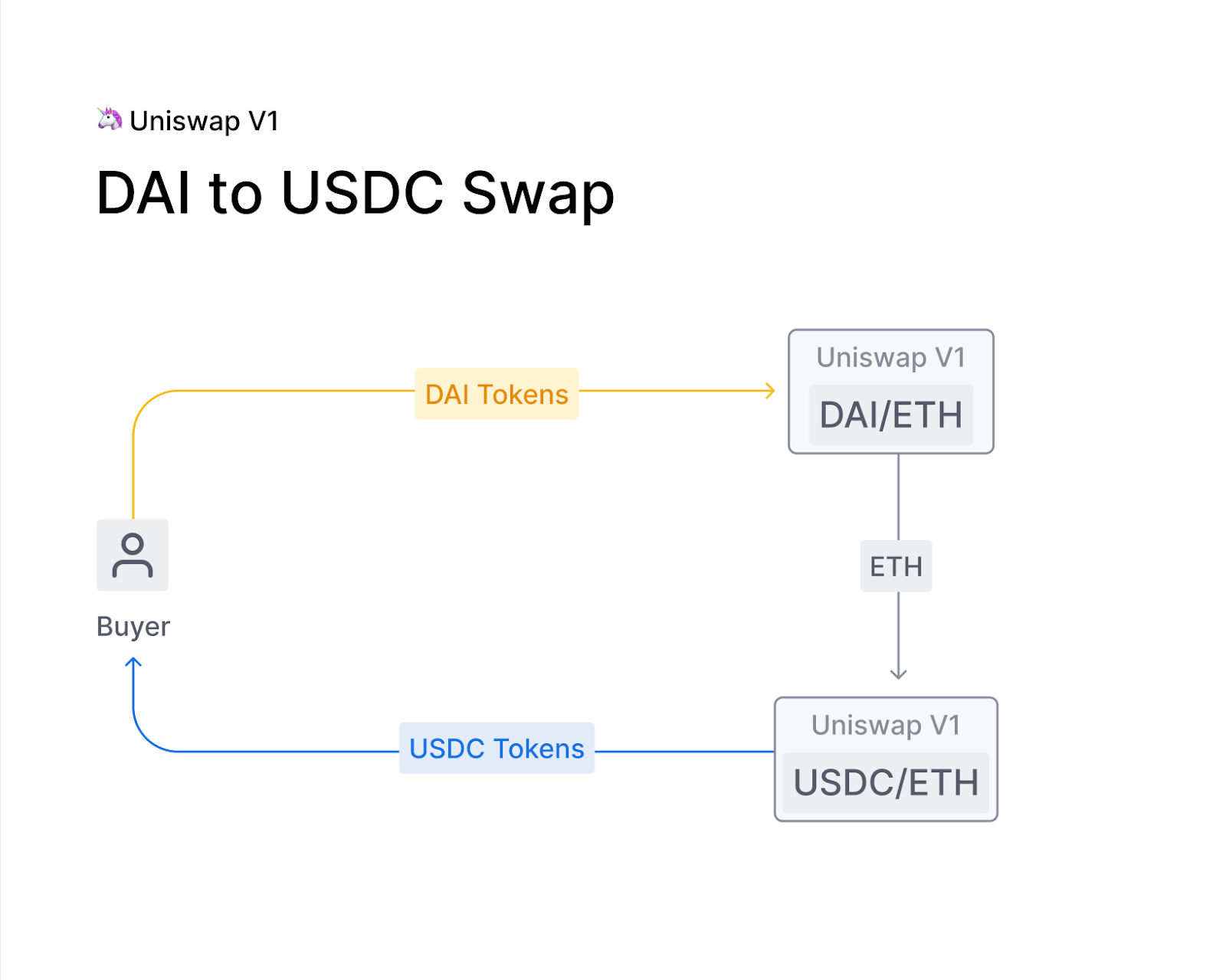
Source: Labs Blog
Moreover, Uniswap V1’s simplistic pricing mechanism proved to be vulnerable to slippage, particularly in instances of large trades as a result of the DEX’s inefficient use of capital in liquidity pools. Slippage refers to the difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which the trade is executed. Due to the constant product formula’s inherent design, the magnitude of a trade exerted a direct influence on the pool’s price, thereby causing significant slippage for sizable orders. Despite these constraints, Uniswap V1’s pioneering approach to decentralised trading captivated the DeFi community and garnered substantial attention. This success served as the impetus for the development of its more advanced and refined successor, Uniswap V2, which was poised to address the limitations of its predecessor and further revolutionise the DeFi landscape.
Uniswap V2
In response to the growing demand for more advanced features and capabilities, Uniswap V2 was launched in May 2020. This new version introduced several key upgrades and improvements over its predecessor, addressing some of the limitations faced by Uniswap V1, and laying the groundwork for an even more robust and versatile decentralised exchange. One of the most significant changes in Uniswap V2 was the introduction of arbitrary ERC-20/ERC-20 token pairs, allowing users to create liquidity pools without the need for ETH as a base currency. This increased flexibility enabled a wider variety of trading pairs, more efficient use of capital, and the possibility for more sophisticated token-based financial products to emerge. With this change, liquidity providers no longer needed to hold ETH to participate in the platform, broadening the appeal of Uniswap to a wider audience and further promoting the growth of the DeFi ecosystem. The arbitrary ERC-20/ERC-20 token pairs also facilitated the creation of novel liquidity pools, enabling more specialised and niche markets to develop, and providing users with additional opportunities for trading and investment. Also, the Uniswap V2 app offers a user-friendly interface for seamless trading on the go.
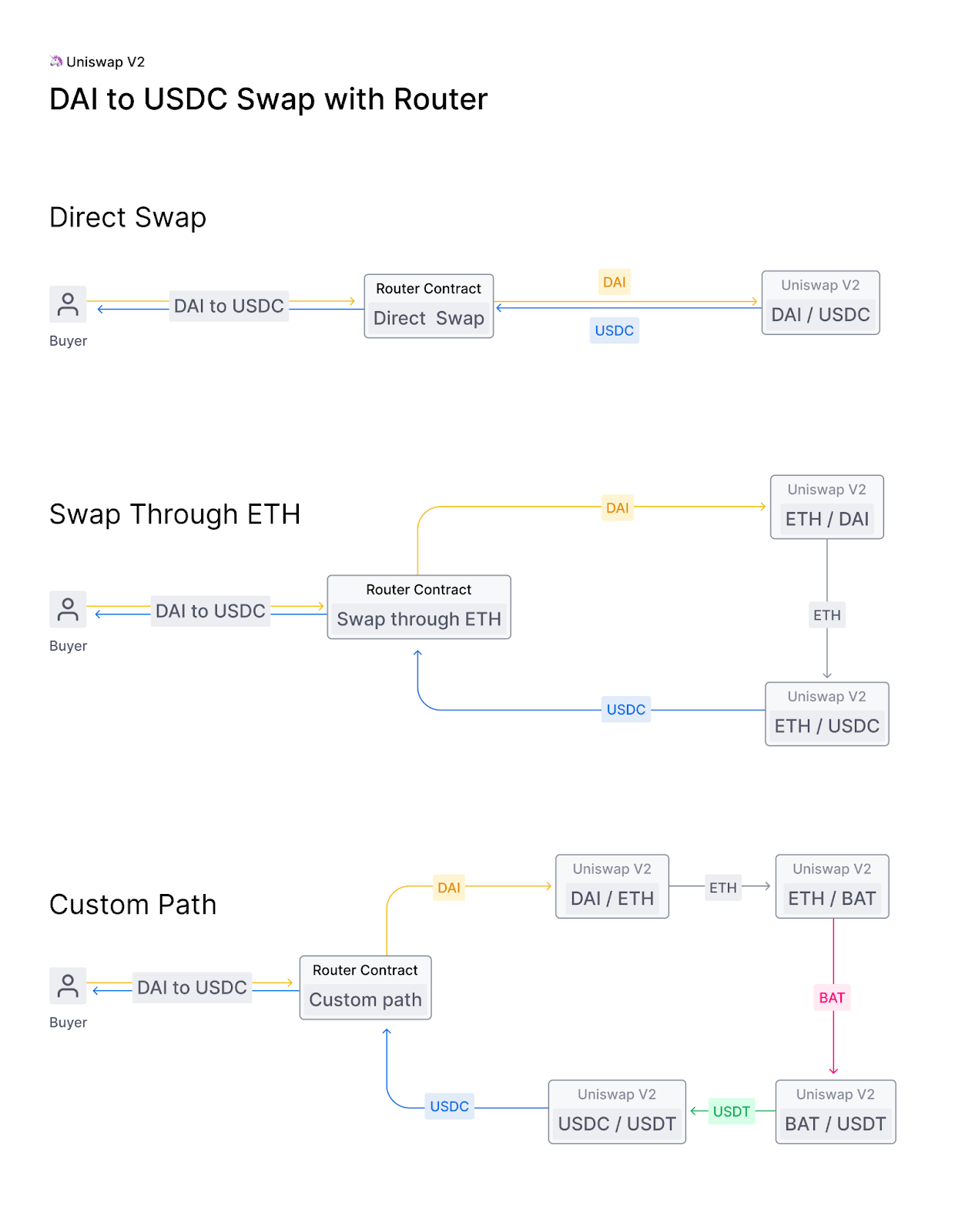
Source: Uniswap Labs Blog
Uniswap V2 also introduced a new price oracle system, which leveraged the platform’s existing liquidity pools to provide more accurate and tamper-resistant price data. This improvement aimed to mitigate the risk of price manipulation and oracle attacks, which had been a concern in the DeFi space. The new price oracle system aggregated data from multiple sources, making it more resistant to manipulation by bad actors. This not only improved the reliability of the platform, but additionally provided a valuable resource for other DeFi projects that required accurate price information for their smart contracts and decentralised applications.
Another notable enhancement was the introduction of flash swaps, a feature that allowed users to borrow tokens from liquidity pools instantaneously, with the condition that they either return the borrowed amount plus fees or provide an equivalent amount of another token by the end of the transaction. This feature opened up new possibilities for arbitrage, liquidations, and other sophisticated trading strategies, offering users more tools and options to capitalise on market inefficiencies. The introduction of flash swaps also contributed to the overall liquidity and efficiency of the Uniswap platform, as it enabled traders to act quickly and decisively in response to changing market conditions.
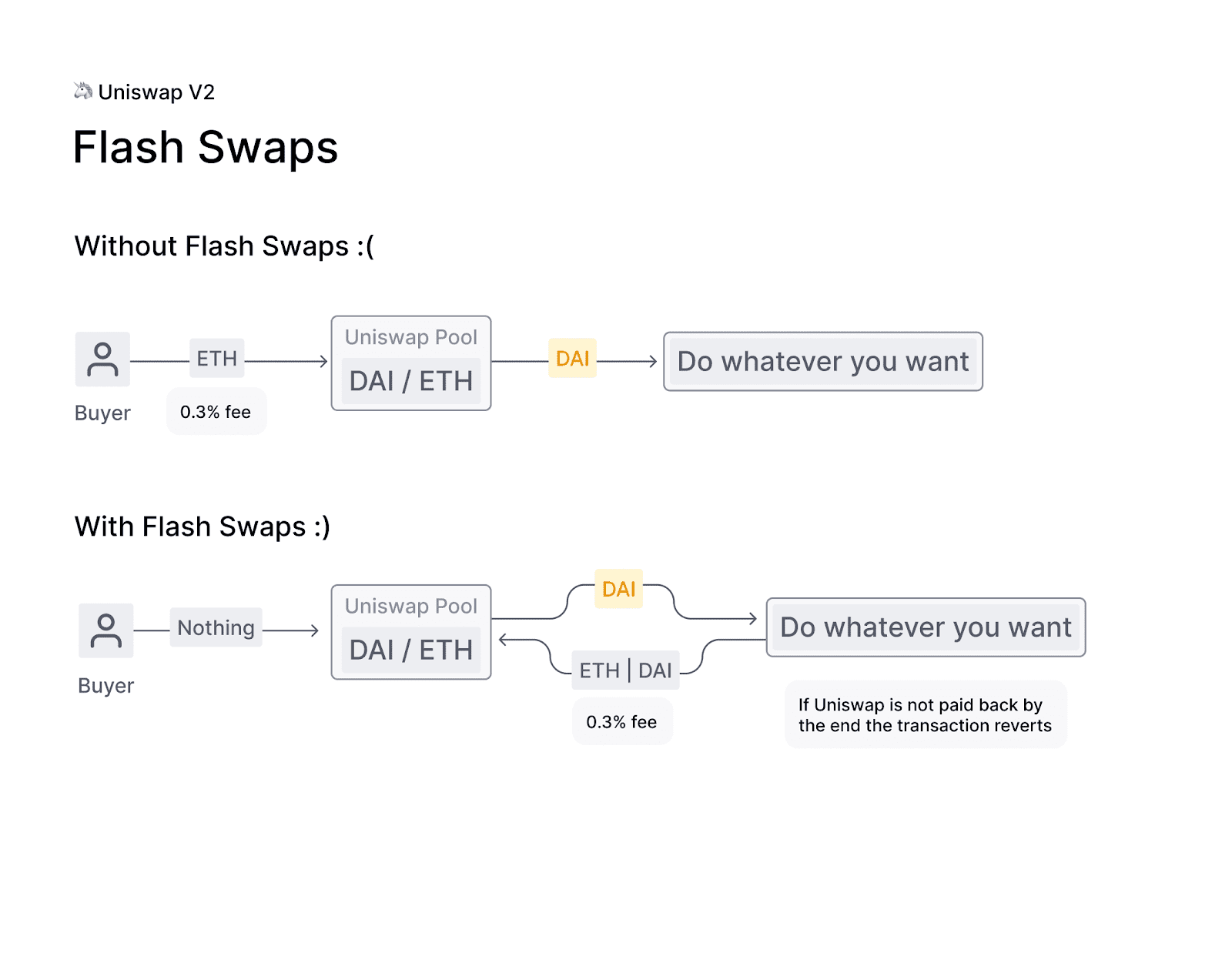
Source: Swapfol
Additionally, Uniswap V2 implemented several optimisations to reduce gas costs and improve transaction efficiency, addressing one of the primary concerns for users in the Ethereum ecosystem. These optimisations included the use of proxy contracts, allowing for the reuse of contract code and reducing the overall size of transactions, as well as more efficient routing algorithms for finding the best trading path between multiple pools. With these improvements, Uniswap V2 aimed to make the trading experience more seamless and cost-effective for its users, while simultaneously easing the burden on the Ethereum network.
Conclusion
Uniswap has been a pioneering force in the world of DEXs, continually innovating and evolving to meet the demands of the growing DeFi ecosystem. Through the development of Uniswap V1 and V2, the protocol has addressed various limitations and challenges faced by traditional, centralised exchanges, and has set new standards for efficiency, security, and decentralisation in digital asset trading. By embracing the power of automated market makers and leveraging smart contracts, Uniswap has offered users a novel solution for trading ERC-20 tokens without the need for intermediaries, while enabling a wide array of advanced features and capabilities. As the blockchain and DeFi landscape continues to mature, it is expected that Uniswap will remain at the forefront of this movement, pushing the boundaries of what is possible and driving further innovation within the space.
About Zerocap
Zerocap provides digital asset liquidity and custodial services to forward-thinking investors and institutions globally. For frictionless access to digital assets with industry-leading security, contact our team at [email protected] or visit our website www.zerocap.com
FAQs
What is Uniswap and how does it differ from traditional exchanges?
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain, designed to facilitate the trading of ERC-20 tokens without the need for a centralized authority. Unlike traditional centralized exchanges, Uniswap leverages the power of automated market makers (AMMs) and smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer trading of digital assets, effectively removing the need for a centralized intermediary. This approach allows users to retain full control of their funds, ensuring they are not exposed to the vulnerabilities associated with centralized custodial solutions.
What are the key differences between Uniswap V1 and V2?
Uniswap V2 introduced several key upgrades and improvements over its predecessor, Uniswap V1. One of the most significant changes was the introduction of arbitrary ERC-20/ERC-20 token pairs, allowing users to create liquidity pools without the need for ETH as a base currency. Uniswap V2 also introduced a new price oracle system, which leveraged the platform’s existing liquidity pools to provide more accurate and tamper-resistant price data. Another notable enhancement was the introduction of flash swaps, a feature that allowed users to borrow tokens from liquidity pools instantaneously.
What is an Automated Market Maker (AMM) in the context of Uniswap?
An Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a type of decentralized exchange protocol that relies on a mathematical formula to price assets. Instead of using an order book like a traditional exchange, assets are priced according to a pricing algorithm. Uniswap uses an AMM model where users trade against a liquidity pool. These pools are filled by liquidity providers who deposit their assets into the pool and receive liquidity tokens in return.
What are the benefits of using Uniswap’s Decentralized Exchange?
Uniswap’s decentralized exchange offers several benefits over traditional centralized exchanges. These include the ability for users to retain full control of their funds, greater privacy due to the absence of extensive Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures, and the potential for reduced risk of hacks and security breaches. Furthermore, Uniswap’s use of AMMs and smart contracts allows for a seamless and efficient trading experience.
What are flash swaps and how do they work in Uniswap V2?
Flash swaps are a feature introduced in Uniswap V2 that allows users to borrow tokens from liquidity pools instantaneously, with the condition that they either return the borrowed amount plus fees or provide an equivalent amount of another token by the end of the transaction. This feature opens up new possibilities for arbitrage, liquidations, and other sophisticated trading strategies, offering users more tools and options to capitalize on market inefficiencies.
DISCLAIMER
Zerocap Pty Ltd carries out regulated and unregulated activities.
Spot crypto-asset services and products offered by Zerocap are not regulated by ASIC. Zerocap Pty Ltd is registered with AUSTRAC as a DCE (digital currency exchange) service provider (DCE100635539-001).
Regulated services and products include structured products (derivatives) and funds (managed investment schemes) are available to Wholesale Clients only as per Sections 761GA and 708(10) of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) (Sophisticated/Wholesale Client). To serve these products, Zerocap Pty Ltd is a Corporate Authorised Representative (CAR: 001289130) of AFSL 340799
All material in this website is intended for illustrative purposes and general information only. It does not constitute financial advice nor does it take into account your investment objectives, financial situation or particular needs. You should consider the information in light of your objectives, financial situation and needs before making any decision about whether to acquire or dispose of any digital asset. Investments in digital assets can be risky and you may lose your investment. Past performance is no indication of future performance.
Like this article? Share
Latest Insights
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 10 March 2026
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 2 March 2026
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Zerocap Launches Institutional OTC Desk for Tokenized Gold Trading
Zerocap’s institutional OTC desk enables investors to access tokenized gold efficiently, supporting portfolio diversification and inflation hedging strategies. The core objective is to provide seamless
Receive Our Insights
Subscribe to receive our publications in newsletter format — the best way to stay informed about crypto asset market trends and topics.


 Share
Share  Tweet
Tweet  Post
Post 