Content
- How do crypto exchanges work?
- Centralised Vs Decentralised Exchanges
- How do exchanges make money?
- Zerocap's Offering
- FAQs
- What is a Cryptocurrency Exchange and How Does it Work?
- What are the Differences Between Centralised and Decentralised Exchanges?
- How do Crypto Exchanges Make Money?
- What are Limit Orders and Market Orders in Crypto Exchanges?
- What Services Does Zerocap Offer?
- About Zerocap
23 Feb, 22
How Crypto Exchanges Work: The mechanisms at play

- How do crypto exchanges work?
- Centralised Vs Decentralised Exchanges
- How do exchanges make money?
- Zerocap's Offering
- FAQs
- What is a Cryptocurrency Exchange and How Does it Work?
- What are the Differences Between Centralised and Decentralised Exchanges?
- How do Crypto Exchanges Make Money?
- What are Limit Orders and Market Orders in Crypto Exchanges?
- What Services Does Zerocap Offer?
- About Zerocap
During the early days of Bitcoin (BTC), there were 2 primary ways to acquire BTC – mine it yourself, or find someone willing to sell it directly to you. Today, the rise of centralised exchanges and institutional adoption has allowed for increased accessibility to cryptocurrencies, facilitating billions of dollars in volume on a daily basis. In this article, we explain the fundamentals of how crypto exchange works; their order books, examples of market executions, comparisons with decentralised exchanges and how these platforms turn a profit on their services. Many often wonder, ‘how do crypto exchanges work?’ or ‘how does a crypto exchange work?’. In this guide, we’ll break down the mechanics behind these platforms.
How do crypto exchanges work?
So how does a crypto exchange work? A cryptocurrency exchange is a marketplace where buyers and sellers can trade one cryptocurrency for another, or exchange it for fiat money. This is primarily done through the utilisation of a live order book. The order book displays live buy and sell orders, directly impacting the exchange rate of the respective cryptocurrency. Since each exchange calculates the price based on its own trading volume, an exchange with more users is likely to provide more market-relevant prices. This is why there are often slight discrepancies in the price of cryptocurrencies amongst different exchanges.
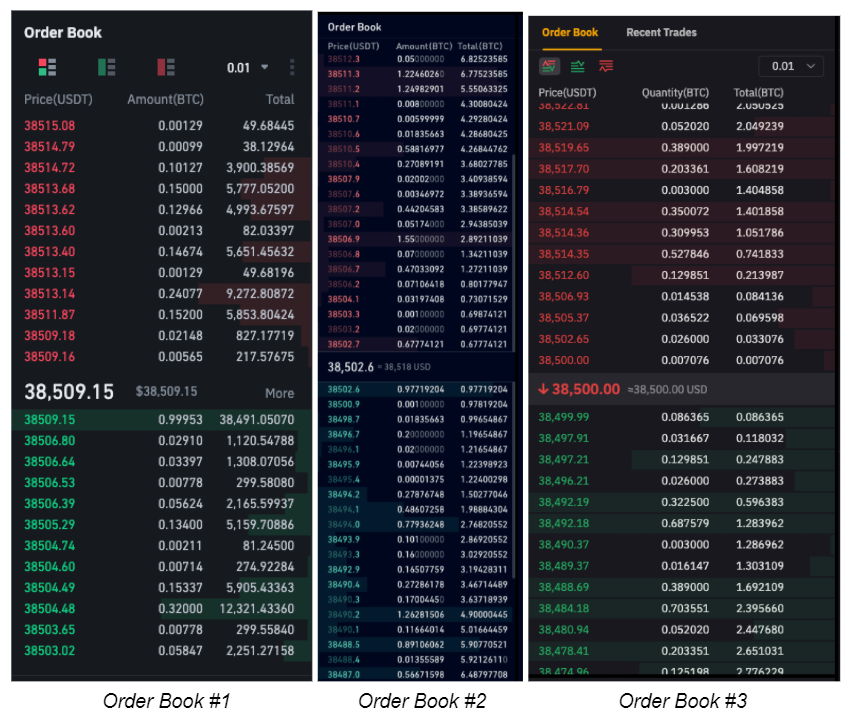
While there are a variety of orders that can be placed on exchanges, only two are widely used – “Limit Order” and “Market Order”. Using Order Book #1 as an example, let’s assume we wanted to buy 0.50 BTC on the BTC/USDT pair. Placing a limit order to purchase 0.50 BTC at 38,500.00 would instruct the exchange to trade your funds at this predefined price or better. This ensures that you will get the desired price, however does not guarantee that your limit order will be executed. For a limit order to be executed, there needs to be a matching buyer/seller who would be willing to trade at that price. In the case of a market order, the exchange will trade your funds at the best possible market price available in the order book. Thus, placing a market order to purchase 0.50 BTC would look like this:
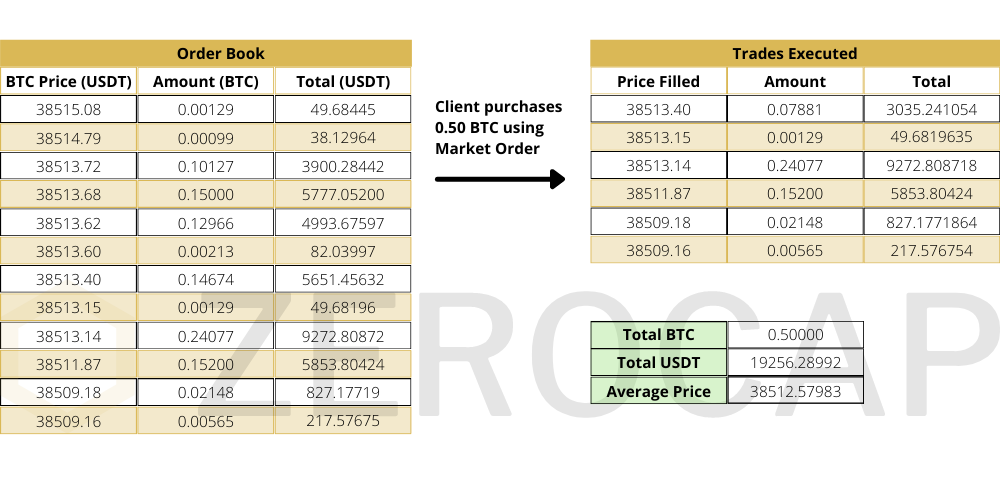
As illustrated above, placing a market order aggregates the best available prices for the respective quantities. In our example, we would end up with 0.50 BTC at an average price of $38,512.58 per BTC, assuming liquidity in the order book remains unchanged. As evident, placing a large block trade on exchanges can be troublesome, as price fluctuations may move against you, resulting in a poor entry/exit point. Thus, high-net-worth investors (HNWI) and family offices prefer to use dedicated wealth management firms such as Zerocap, as we offer personal relationship managers, OTC trading services, deep liquidity, tight spreads across pairs and an overall comprehensive white glove service. Zerocap also works with crypto exchanges to improve liquidity on their exchange through a service called market making, read more here.
Centralised Vs Decentralised Exchanges
Whilst most investors are familiar with centralised exchanges as they offer a familiar experience to traditional trading platforms, cryptocurrency investors have access to their decentralised counterparts which offer unique benefits. Decentralised exchanges (DEX’s) are peer-to-peer marketplaces built on smart contracts, through which transactions are facilitated without an intermediary. Allowing users to maintain custody of their assets, DEX’s are built on leading blockchains such as Ethereum, embracing the trustlessness and privacy characteristics of blockchain technology.
The primary differentiators between these two exchange types are as follows:
- Trading Options: Centralised exchanges (CEX) typically offer a wider range of choices including options, staking, lending, futures and airdrops, whereas decentralised exchanges (DEX) often have thinner liquidity, and may be subject to smart contract or counterparty risk.
- Listed Coins: As there is no verification process required to be listed on a DEX, users can essentially trade all crypto assets on DEX’s, whereas CEX’s typically follow a stringent listing process and offer a limited number of coins.
- KYC: Being decentralised, users can use any DEX without a KYC process. However, since CEX’s are heavily monitored by regulators, they usually require users to pass through several identity verification processes before trading.
- Accessibility: CEX’s are significantly more user friendly, while offering customer support 24/7. As DEX’s do not involve any middlemen, the options offered on their user interface can be limited, and difficult to navigate for novice traders.
The choice between a CEX or DEX relies on the trader’s purpose and their preferences. While CEX’s may be attractive for beginner traders seeking a friendly interface with user support, the lack of regulatory requirements around DEX’s and accessibility to smallcap projects may be alluring for privacy concerned and risk-loving investors. Enabling access to both CEX’s and DEX’s, Zerocap is able to cater to client needs, providing access to tokens only available on DEX’s without the associated risks, further backed by institutional-grade custody services offering robust insurance to prevent misuse of funds.
How do exchanges make money?
The most popular method for monetizing centralised exchanges is through charging commissions on their platform. For every trade that occurs on the exchange, a set commission rate, as low as 0.1% may be charged. Due to increased competition, new exchanges struggle with thin liquidity during consolidated markets, and thus opt for charging listing fees for coins to be listed on their exchange. This, in addition to facilitating Initial Exchange Offerings (IEO’s) acts as an alternative revenue stream for exchanges. Lastly, popular exchanges opt to issue native exchange tokens, offering fee incentives to holders on their exchanges in an attempt to foster a native ecosystem.
Zerocap’s Offering
With almost 400 crypto exchanges available worldwide, cryptocurrency exchanges have simplified the onboarding process for individuals tremendously, however offer almost identical services across platforms.
With the ability to access the top exchanges worldwide, Zerocap differentiates itself from retail exchanges, offering access to a broader range of assets as opposed to being constrained by a single exchange. Additionally, the inclusion of institutionalised financial instruments in our offerings, coupled with aggregated liquidity and post-trade settlements distinguishes and enables us to cater to HNWI and family offices, as one of the only Australian firms to do so.
We can trade any cryptocurrency available (except privacy coins) on request from our customers – simplifying access to crypto liquidity through our straightforward Wealth Portal. Clients have direct access to our team to request quotes, purchase, sell, stake, yield, add insurance and more.
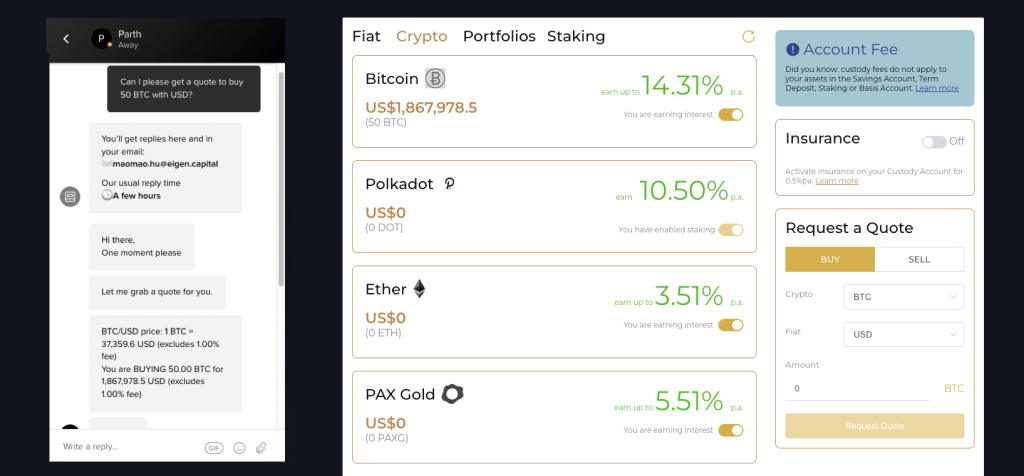
FAQs
What is a Cryptocurrency Exchange and How Does it Work?
A cryptocurrency exchange is a marketplace where buyers and sellers can trade one cryptocurrency for another, or exchange it for fiat money. This is primarily done through the use of a live order book, which displays live buy and sell orders, directly impacting the exchange rate of the respective cryptocurrency. The price is calculated based on the exchange’s own trading volume, which is why there are often slight discrepancies in the price of cryptocurrencies amongst different exchanges.
What are the Differences Between Centralised and Decentralised Exchanges?
Centralised exchanges (CEX) offer a wider range of choices including options, staking, lending, futures, and airdrops, and typically follow a stringent listing process. On the other hand, decentralised exchanges (DEX) are peer-to-peer marketplaces built on smart contracts, allowing users to maintain custody of their assets. DEXs offer unique benefits such as privacy and access to all crypto assets, but may have thinner liquidity and be subject to smart contract or counterparty risk.
How do Crypto Exchanges Make Money?
The most popular method for monetizing centralised exchanges is through charging commissions on their platform. For every trade that occurs on the exchange, a set commission rate may be charged. Some exchanges also charge listing fees for coins to be listed on their exchange, facilitate Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs), or issue native exchange tokens offering fee incentives to holders.
What are Limit Orders and Market Orders in Crypto Exchanges?
Limit orders and market orders are two widely used types of orders on exchanges. A limit order instructs the exchange to trade your funds at a predefined price or better, ensuring that you get the desired price. However, it does not guarantee that your limit order will be executed. A market order, on the other hand, instructs the exchange to trade your funds at the best possible market price available in the order book.
What Services Does Zerocap Offer?
Zerocap offers access to a broader range of assets as opposed to being constrained by a single exchange. We provide services such as personal relationship managers, OTC trading services, deep liquidity, tight spreads across pairs, and an overall comprehensive white glove service. We also offer access to both CEX’s and DEX’s, providing access to tokens only available on DEX’s without the associated risks, further backed by institutional-grade custody services offering robust insurance to prevent misuse of funds.
About Zerocap
Zerocap provides digital asset investment and custodial services to forward-thinking investors and institutions globally. Our investment team and Wealth Platform offer frictionless access to digital assets with industry-leading security. To learn more, contact the team at hello@zerocap.com or visit our website www.zerocap.com
Like this article? Share
Latest Insights
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 21st July 2025
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Weekly Crypto Market Wrap: 14th July 2025
Zerocap is a market-leading digital asset firm, providing trading, liquidity and custody to forward-thinking institutions and investors globally. To learn more, contact the team at
Zerocap selects Pier Two to offer institutional staking yields
Institutional clients gain secure, non-custodial access to native crypto yields with top-tier infrastructure Leading digital asset firm Zerocap has selected global institutional staking provider Pier
Receive Our Insights
Subscribe to receive our publications in newsletter format — the best way to stay informed about crypto asset market trends and topics.



 Share
Share  Tweet
Tweet  Post
Post 